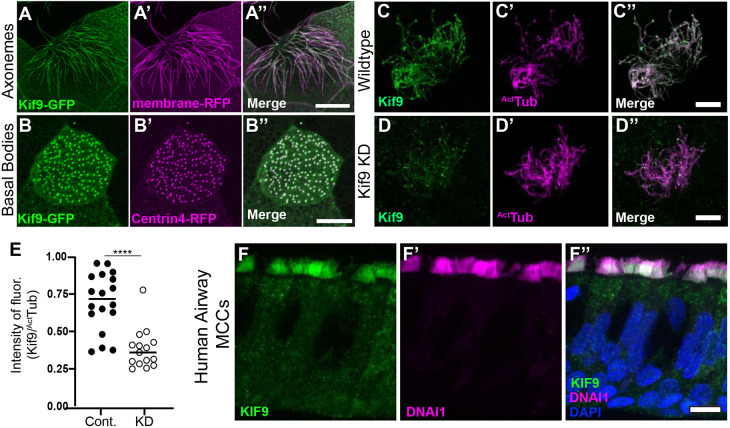
Fig. 1.
Kif9 localization to motile cilia. (A–A″) Kif9–GFP construct localizes to Xenopus multiciliated cells in the axonemes. Kif9–GFP is in green (A), membrane–RFP is in magenta (A′). (B–B″) The Kif9–GFP construct localizes to basal bodies of multiciliated cells in Xenopus. Kif9–GFP in green (B), Centrin4–RFP in magenta (B′). (C–C″) Kif9 antibody (green) confirms localization to Xenopus axonemes. Kif9 in green (C) and acetylated tubulin (ActTub) in magenta (C′). (D–D″) Knockdown of Kif9 with 15 ng of MO reduces the level of Kif9 (green) in the cilium. (E) Quantification of Kif9 staining intensity over the intensity of acetylated tubulin in control and MO-injected frogs. (F–F″) Kif9 immunostaining in human airway multiciliated cells (MCCs). (F) Kif9 immunostaining (green). (F′) DNAI immunostaining (magenta). (F″) Merge of F–F′ with DAPI. Images are representative of 30 different cells imaged from three independent experiments with at least 10 different embryos imaged for each replicate. Scale bars: 10 µm.