Fig. 4 |. Model of the role of somatic mutations in AD pathogenesis.
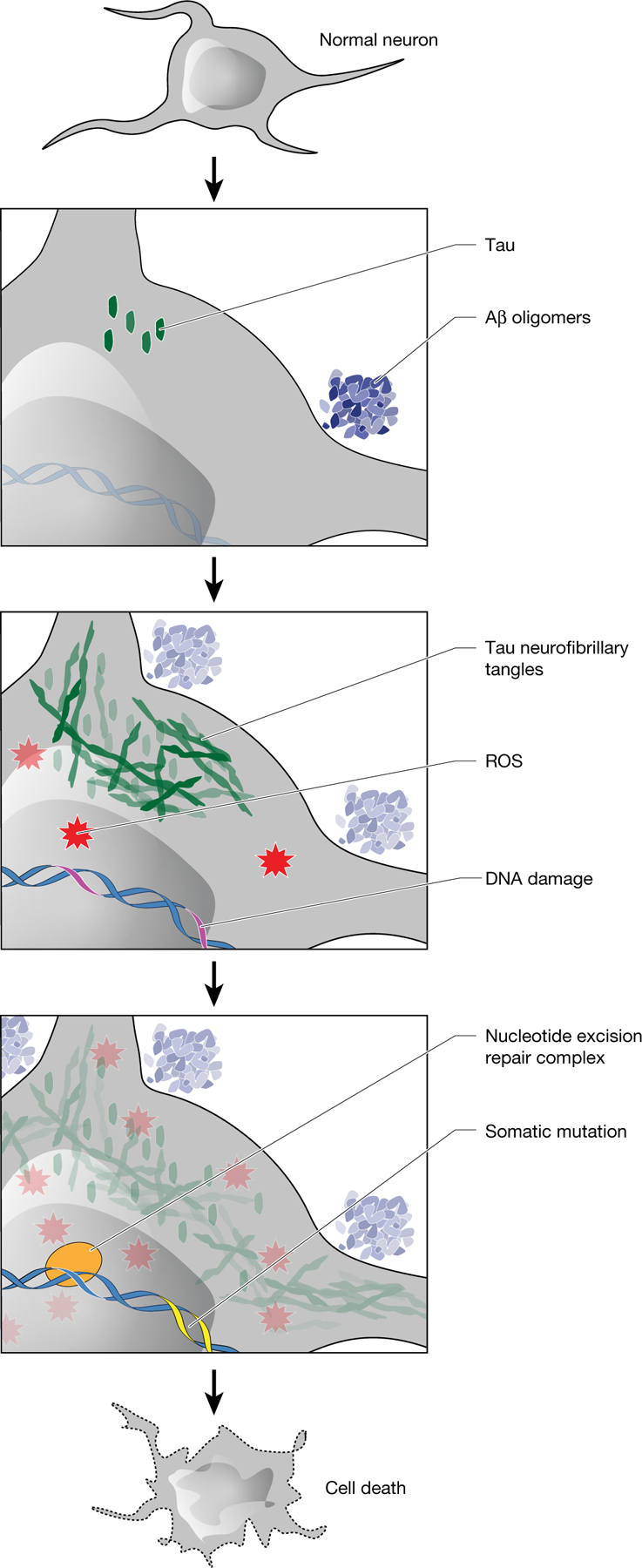
Amyloid-β(Aβ) oligomers initiate a cascade of events, including the conversion of tau to neurofibrillary tangles and the accumulation of ROS. After DNA damage by ROS or other mutagens, somatic mutations develop with characteristic features of signature C. NER affects the strand and gene distribution of somatic mutations, and rare base misincorporation during repair may also have a role in the progression from DNA damage to mutation. These somatic mutations stand to increase cellular vulnerabilitybymechanismsincludinggeneinactivationandneoantigenpresentation.
