Fig. 1.
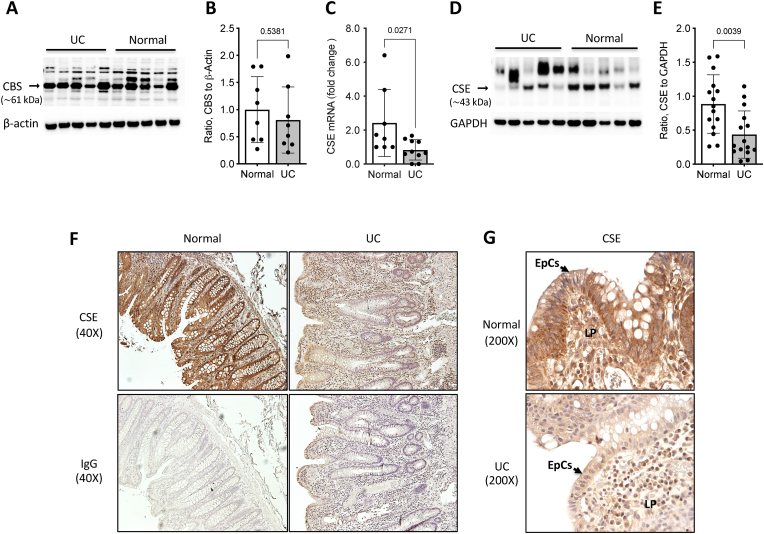
Mucosal biopsy specimens from patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) show reduced CSE expression. A) Representative Western blot comparing CBS protein expression in colon mucosa biopsies from patients with ulcerative colitis (UC) and healthy individuals (Normal). B) Results of densitometric analysis of CBS expression in UC (n = 8) and normal (n = 8) mucosal specimens. C) Reverse Transcription-quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR) assay comparing CSE mRNA levels in mucosal biopsies from normal and patients with UC. D) Representative Western blot comparing CSE protein levels in colon mucosa biopsies from healthy and UC patients. E) Results of densitometric analysis of CSE expression in UC (n = 14) and normal (n = 14) mucosal specimens. Statistical analyses of data in panels B, C, and E: D'Agostino & Pearson Normality test, Unpair t-test, two-tailed, error bars represent standard deviation, p values shown. F&G) Immunohistochemical staining for CSE protein (brown) using formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue sections (5 μm thickness) from representative healthy and UC biopsy specimens. The sections were counterstained with hematoxylin (purple) to reveal tissue architecture. Non-specific antibody binding was determined by immunostaining serial tissue sections with an isotype-matched rabbit immunoglobulin (IgG) at the same concentration (2 ng/μL) as the primary rabbit anti-CSE antibody. Images were taken at 40X (F) and 200× (G) magnification (EpCs: epithelial cells; LP: lamina propria). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)