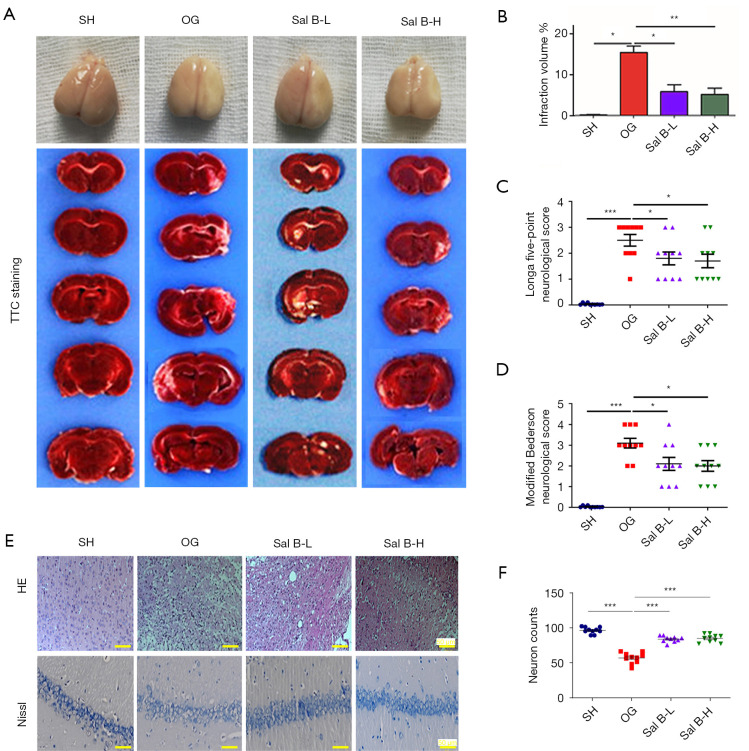
Figure 1.
Sal B attenuates ischemic brain injury in MCAO rats. (A) Representative images of serial brain sections showing ischemic infarct in white as determined by TTC staining in the four rat groups: SH; OG; Sal B-L (10 mg/kg/d); Sal B-H (20 mg/kg/d). (B) Quantitative analysis of the infarction volume. (C) Quantitative analysis of neurological outcomes of MCAO rats as measured with a 5-point NSS scale. (D) Quantitative analysis of neurological outcomes of MCAO rats as measured with modified Bederson scores. (E) Representative images of the cerebral cortex region with H&E staining (top row). Representative images of the hippocampal region with Nissl staining (bottom row) (n=6 per group, scale bar: 50 µm). (F) Quantification of neuron counts were shown using mean ± SD. *, P<0.05, **, P<0.01, ***, P<0.001. Sal B, salvianolic acid B; MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; TTC, triphenyltetrazolium chloride; SH, sham operation rats intraperitoneally injected with saline; OG, rats with MCAO intraperitoneally injected with saline; Sal B-L, MCAO rats intraperitoneally injected with a low (L) dose of Sal B; Sal B-H, MCAO rats intraperitoneally injected with a high (H) dose of Sal B; NSS, neurological severity score.