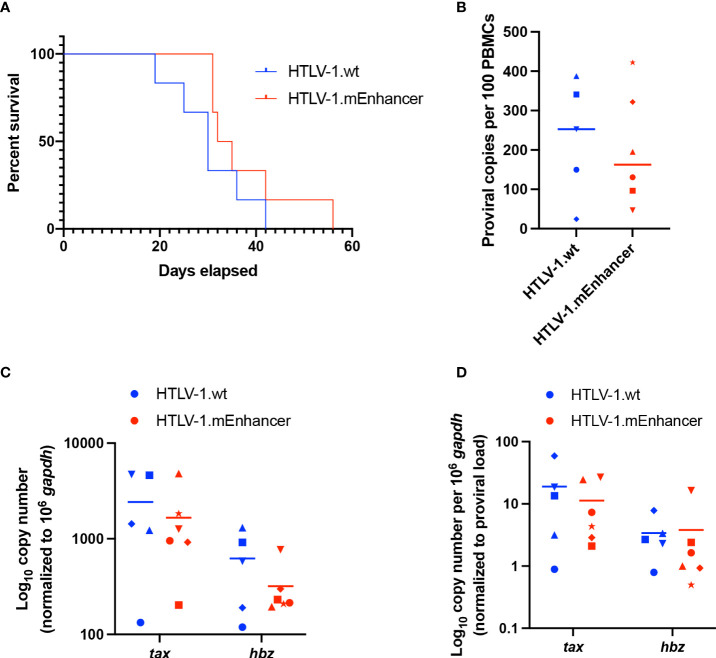
Figure 5.
Loss of enhancer element has no effect on disease progression in HIS mice. Sub-lethally irradiated neonatal NSG received liver injections of 3 x 104 to 1 x 105 of CD34+ HUSC. 10 weeks after HUSC engraftment, mice were inoculated intraperitoneally with 1 x 107 lethally irradiated 729 HTLV-1.wt or 729 HTLV-1.mEnhancer producer cells. (A) HTLV-1 infection induces lymphoproliferative disease in the mice, and survival rate was determined for animals inoculated with wt compared to mEnhancer virus. Mice were euthanized according to early removal criteria defined in the approved animal protocol. Statistical significance was determined by Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. (B) Genomic DNA was extracted from PBMCs isolated from mouse spleens and used for qPCR to detect proviral load using primers targeting HTLV-1 Gag/pol. Statistical significance was determined by Welch’s unpaired t test. (C) RNA extracted from hPBMCs was subjected to cDNA synthesis followed by qPCR to detect viral gene expression. Data are shown normalized to 1 x 106 hgapdh copies. (D) The levels of viral transcripts were evaluated by normalizing Tax or Hbz copies per 106 hgapdh to proviral load. Unique symbols in (B–D) represent proviral load, gene expression, and viral transcripts per proviral copy number, respectively, in a single inoculated mouse and bars represent the mean. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired t-test.