Figure 1. PP2A inhibits DLK signaling to restrain synaptic terminal growth at the Drosophila NMJ.
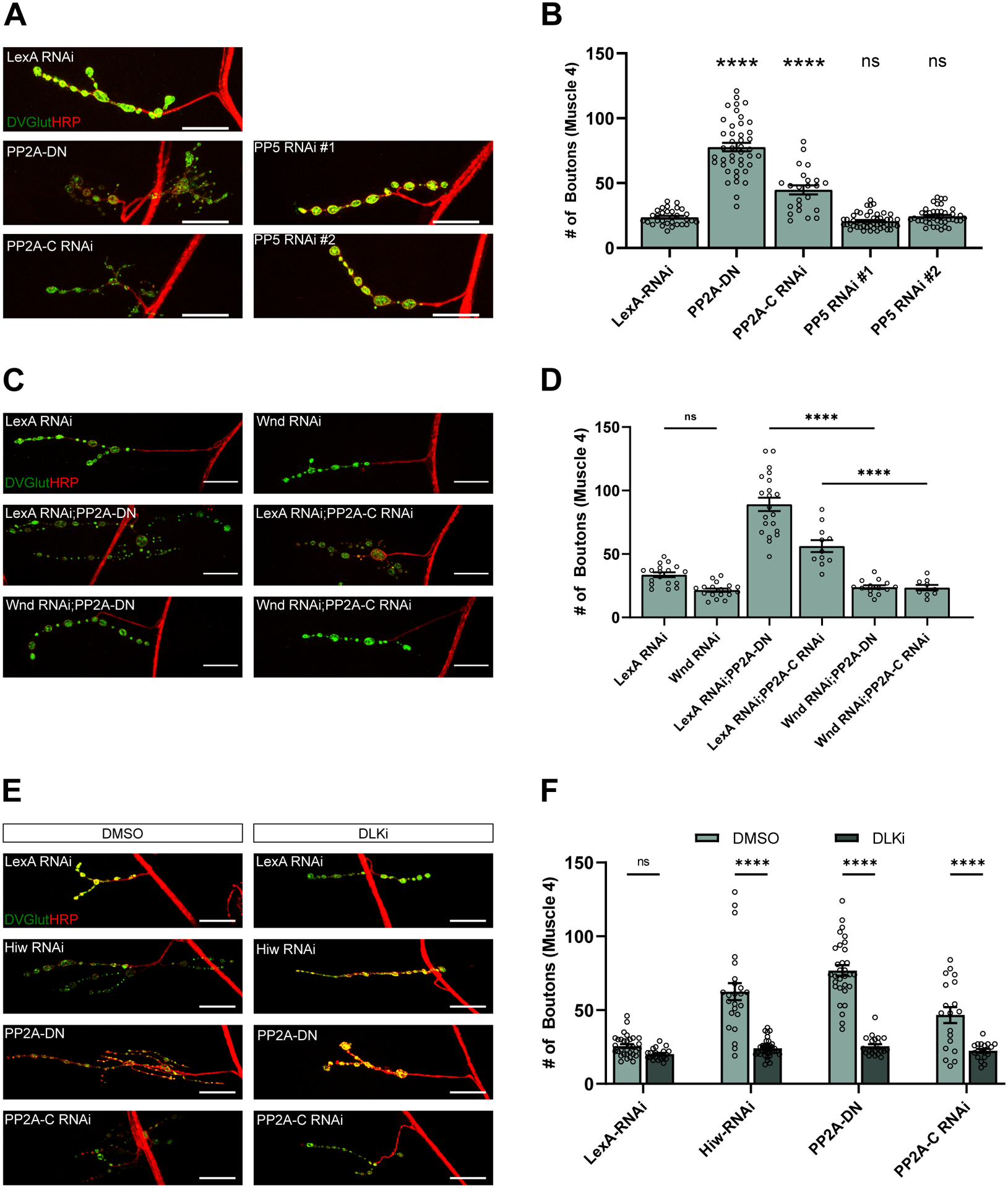
(A) Representative images of synaptic terminal overgrowth at the NMJ of third instar larvae. Transgenes are being driven by DVGlutgal4 in the presence of UAS-Dcr to improve RNAi knockdown. Tissue is stained for the presynaptic marker DVGlut (green) and the nerve membrane with anti-HRP (red). Scale bar is 25 μM.
(B) Quantification of the mean (± SEM) number of boutons on the type 1b synapse on muscle 4. Expression of PP2A-DN or PP2A-C RNAi significantly increases the number of boutons compared to an animal expressing a control RNAi (p < 0.0001) as measured by a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test. Expression of either of two RNAis against PP5 is not significantly different from animals expressing a control RNAi (p = 0.8450 and p = 0.9991 respectively). Data points represent biological replicates of individual neurons analyzed at the level of the NMJ.
(C) Representative images of the suppression of synaptic terminal overgrowth from PP2A inhibition by Wnd RNAi in third instar larvae. Transgenes are being driven by DVGlutgal4 in the presence of UAS-Dcr to improve RNAi knockdown. Tissue is stained for the presynaptic marker DVGlut (green) and the nerve membrane with anti-HRP (red). Scale bar is 25 μM.
(D) Quantification of the mean (± SEM) number of boutons in larvae driving constructs using DVGlutgal4 and UAS-Dcr. Co-expression of Wnd RNAi compared to co-expression a LexA RNAi control with PP2A inhibition significantly suppresses an increase in synaptic bouton number (p < 0.0001 for PP2A-DN and p = 0.0004 for PP2A-C RNAi). There is no significant difference between the number of boutons in flies expressing LexA RNAi and Wnd RNAi (p = 0.1029). Data points represent biological replicates of individual neurons analyzed at the level of the NMJ. Statistical significance was measured by a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.
(E) Representative images of the suppression of synaptic terminal overgrowth in third instar larvae from PP2A inhibition by DLK inhibitor (GNE-3511, 35 μM). Transgenes are being driven by DVGlutgal4 in the presence of UAS-Dcr to improve RNAi knockdown. Tissue is stained for the presynaptic marker DVGlut (green) and the nerve membrane with anti-HRP (red). Scale bar is 25 μM.
(F) Quantification of the mean (± SEM) number of boutons in larvae fed either DMSO or DLK inhibitor (GNE-3511, 35 μM). Being raised on DLKi as compared to DMSO significantly suppressed synaptic overgrowth in larvae expressing Hiw RNAi (p < 0.0001), PP2A-DN (p <0.0001), or PP2A-C RNAi (p <0.0001) under a DVGlutgal4 with UAS-Dcr. Data points represent biological replicates of individual neurons analyzed at the level of the NMJ. Statistical significance was determined using a two-way ANOVA with Šídák’s multiple comparisons test.
