Figure 4. PP2A inhibition triggers DLK-dependent neuronal cell death independent of Tau.
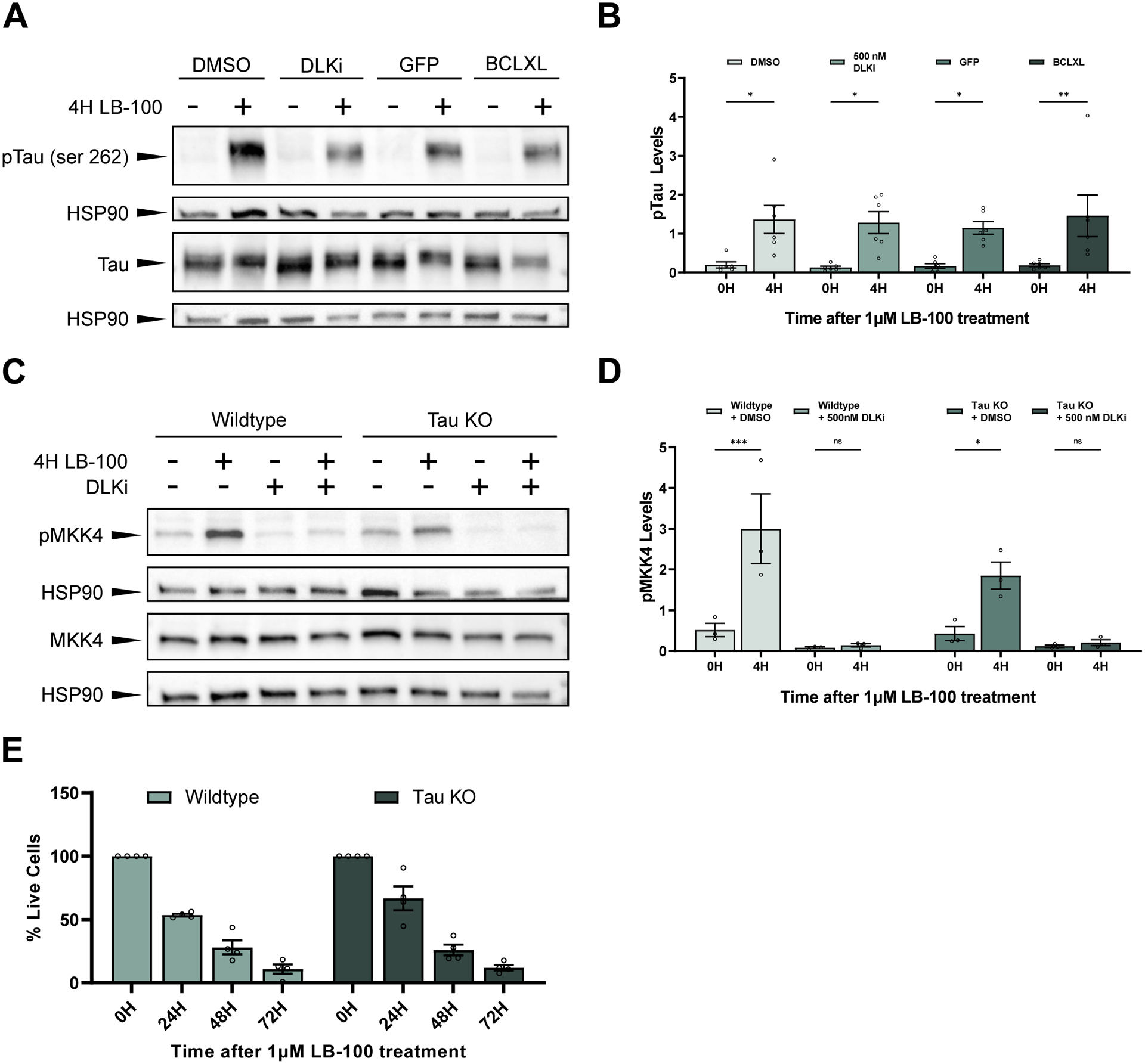
(A) Representative western blots stained with pTau (serine 262), total Tau (Tau-5), and HSP90. Primary mouse cortical neurons were treated with 1 μM LB-100 for 4 hours. Cells were expressing either a GFP control or BCLXL or were treated 30 minutes before LB-100 treatment with either DMSO or 500 nM DLKi.
(B) Quantification of the mean (± SEM) relative levels of pTau (serine 262) at 0 or 4 hours following exposure to 1 μM LB-100 in primary mouse cortical neurons. Cells were expressing a GFP control or the anti-apoptotic protein BCLXL or were pre-treated 30 minutes before the addition of LB-100 with DMSO or 500 nM DLKi. Data points represent biological replicates of separate neuronal preps. There was a significant increase in pTau levels in cells 4 hours after LB-100 treatment as measured by two-way ANOVA with Šídák’s multiple comparisons test (p = 0.043503 for GFP-expressing cells, p = 0.004952 for BCLXL-expressing cells, p = 0.011190 for DMSO treated cells, and p = 0.012500 for DLKi treated cells).
(C) Representative western blots showing pMKK4 (serine 257/threonine 261), MKK4, and HSP90 levels in primary cortical neurons from wildtype (C57BL/6) or Tau KO mice treated with 1 μM LB-100 for 4 hours. Cells were pre-treated 30 minutes before the addition of LB-100 with either DMSO or 500 nM DLKi.
(D) Quantification of the mean (± SEM) relative levels of pMKK4 following LB-100 treatment in primary cortical neurons from wildtype (C57BL/6) and Tau KO mice pre-treated with DMSO or 500 nM DLKi. Both wildtype and Tau KO mice show a significant increase in pMKK4 following LB-100 treatment (p = 0.000342 and p = 0.034282 respectively), while neurons pre-treated with DLKi showed no difference in pMKK4 levels following LB-100 treatment (p = 0.999909 for wildtype neurons and p = 0.999612 for Tau KO neurons). Data points represent biological replicates of separate neuronal preps. Statistical significance was measured by two-way ANOVA with Šídák’s multiple comparisons test.
(E) Quantification of mean (± SEM) relative amount of living cells as measured by an MTT assay in primary cortical neurons from wildtype and Tau KO mice following treatment with 1 μM LB-100 for 0, 24, 48, and 72 hours. Each data point represents a biological replicate which is the average of at least 4 technical replicates. There is no significant difference in the percentage of living cells at 24, 48, or 72 hours after LB-100 treatment between wildtype and Tau KO neurons (p = 0.169797, p = 0.996235, and p = 0.999647 respectively). Statistical significance was measured using a two-way ANOVA with Šídák’s multiple comparisons test.
