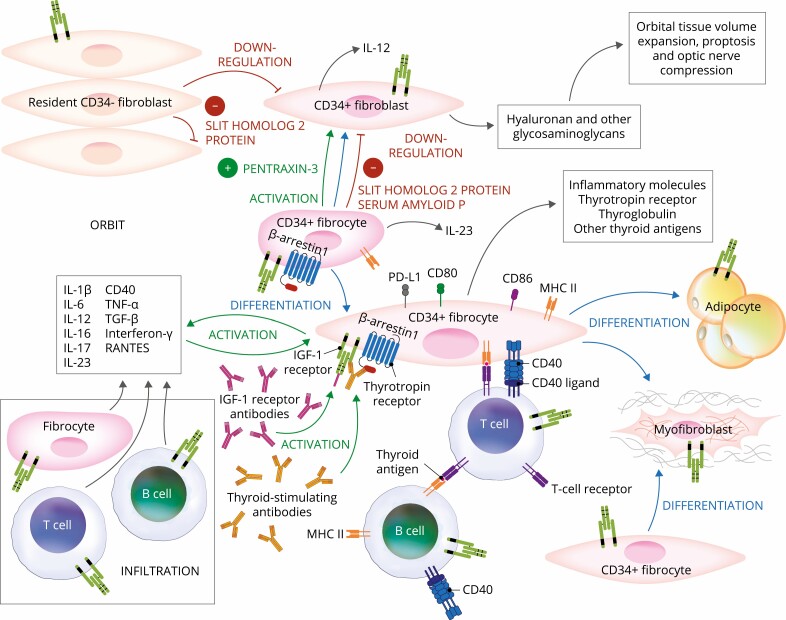
Figure 2.
Proposed theoretical model of thyroid eye disease (TED) pathogenesis. Orbital fibroblasts exhibiting robust responses to inflammatory mediators appear to represent the central effector cells. CD34+ fibroblasts derived from CD34+ CXCR4+ collagen 1 + fibrocytes, monocyte-derived progenitors traffic from bone marrow to the TED orbit. Fibrocytes express several thyroid-specific proteins, including thyrotropin receptor (TSHR), thyroglobulin, thyroperoxidase, and sodium-iodide symporter and express class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC). Fibrocytes and orbital fibroblasts undergo differentiation into myofibroblasts and adipocytes. Slit2 expressed and released by CD34- fibroblasts down regulates expression of many genes expressed by fibrocytes and CD34+ fibroblasts. Interleukins 1β, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, and 23, tumor necrosis factor α, and Regulated on Activation, Normal T Expressed and Secreted (RANTES), CXCL-12, and CD40-CD154 are expressed in the TED orbit by various cell types and contribute to the inflammatory milieu. CD34+ and CD34- orbital fibroblasts cell-surface display insulin-like growth factor-I receptor (IGF-IR) and express 3 mammalian hyaluronan synthase isoenzymes and UDP glucose dehydrogenase and synthesize hyaluronan. This glycosaminoglycan underlies in part orbital tissue expansion in TED. Hyaluronan synthesis localizes primarily to CD34- orbital fibroblasts.