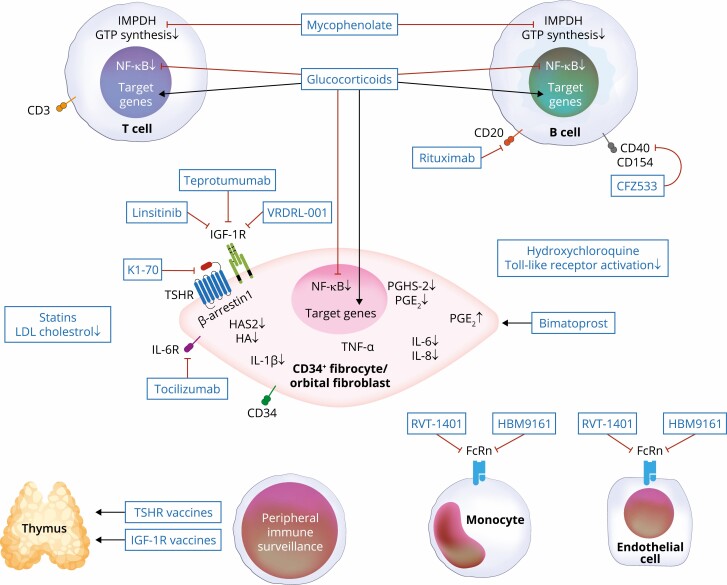
Figure 4.
Putative molecular targets for current medical therapies and those under development. Glucocorticoid steroids target many cell types, where they induce several target genes while inhibiting the expression of others. Many of their anti-inflammatory actions are mediated through nuclear factor-κB. Other agents are more target-specific, such as mycophenolate (targets inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase [IMPDH] and GTP synthesis in lymphocytes), rituximab (anti-CD20 displayed on B cells), tocilizumab (IL-6 receptor inhibitor), teprotumumab, VRDN-001, linsitinib (IGF-IR inhibitors), K1-70 (TSHR inhibitor), RVT-1401, HBM9161 (FcRn antagonists), CFZ533 (anti-CD40 antagonist), and TSHR and IGF-IR vaccines. It is possible that additional, as-yet unidentified targets may play important roles in mediating clinical responses.