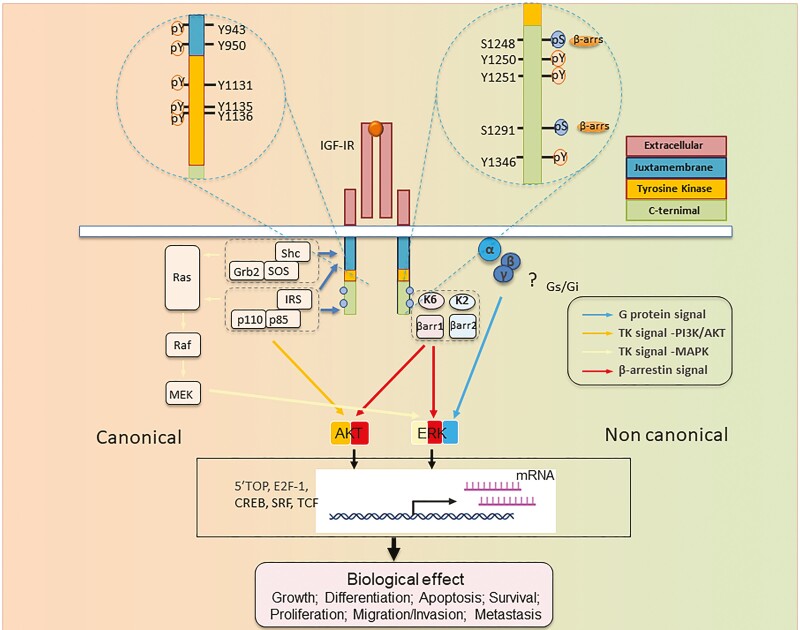
Figure 2.
Structure-function relationship of IGF-I receptor (IGF-IR) informing RTK/GPCR dualism. IGF-IR is annotated with numbered aa residues. Known key residues/sites of posttranslational modifications (PTMs) as determinant substrates/adaptor protein binding within β-subunit, thus controlling both canonical RTK signaling (left) and noncanonical GPCR-like signaling. IGF-IR kinase-dependent signaling pathways: IGF-I (or IGF-II) binding to IGF-IR promotes intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity and autophosphorylation. Activated receptor can recruit and phosphorylate substrates such as IRS and Shc. Phosphorylated tyrosine 950 within Asn-Pro-X-Tyr juxta membrane motif is essential for insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS1)/IRS-2 and SHC-transforming protein (Shc) recruitment. Tyrosine phosphorylation of IRS and Shc proteins leads to as Grb2 and PI 3-kinase (p110/p85) binding. These protein associations induce downstream signaling activation, primarily through the rat sarcoma virus/Raf/MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways, which in turn activate transcription factors coordinating downstream IGF biological effects. In addition to kinase signaling, agonist-induced IGF-IR stimulation results in noncanonical GPCR signaling through heterotrimeric G proteins (α, β, γ) (? = not yet fully understood pathways), followed by rapid IGF-IR phosphorylation by G protein-coupled receptor kinases (GRKs, K2, K6) at serine residues within the C-terminus. Serine-phosphorylated receptors present high-affinity binding sites for multifunctional adaptor protein β-arrestin 1/2 (βarr1/2). βarr recruitment: βarr acquires an active conformation following IGF-IR binding with MAPK pathway scaffold components. These events result in second wave IGF-IR kinase-dependent MAPK/ERK signaling activation. Abbreviations: Akt, protein kinase B; ERK, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; IGF-IR, IGF receptor; P = major phosphorylation sites; IRS, insulin receptor substrate; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase/Erk kinase; Shc, Src homology and collagen domain protein.