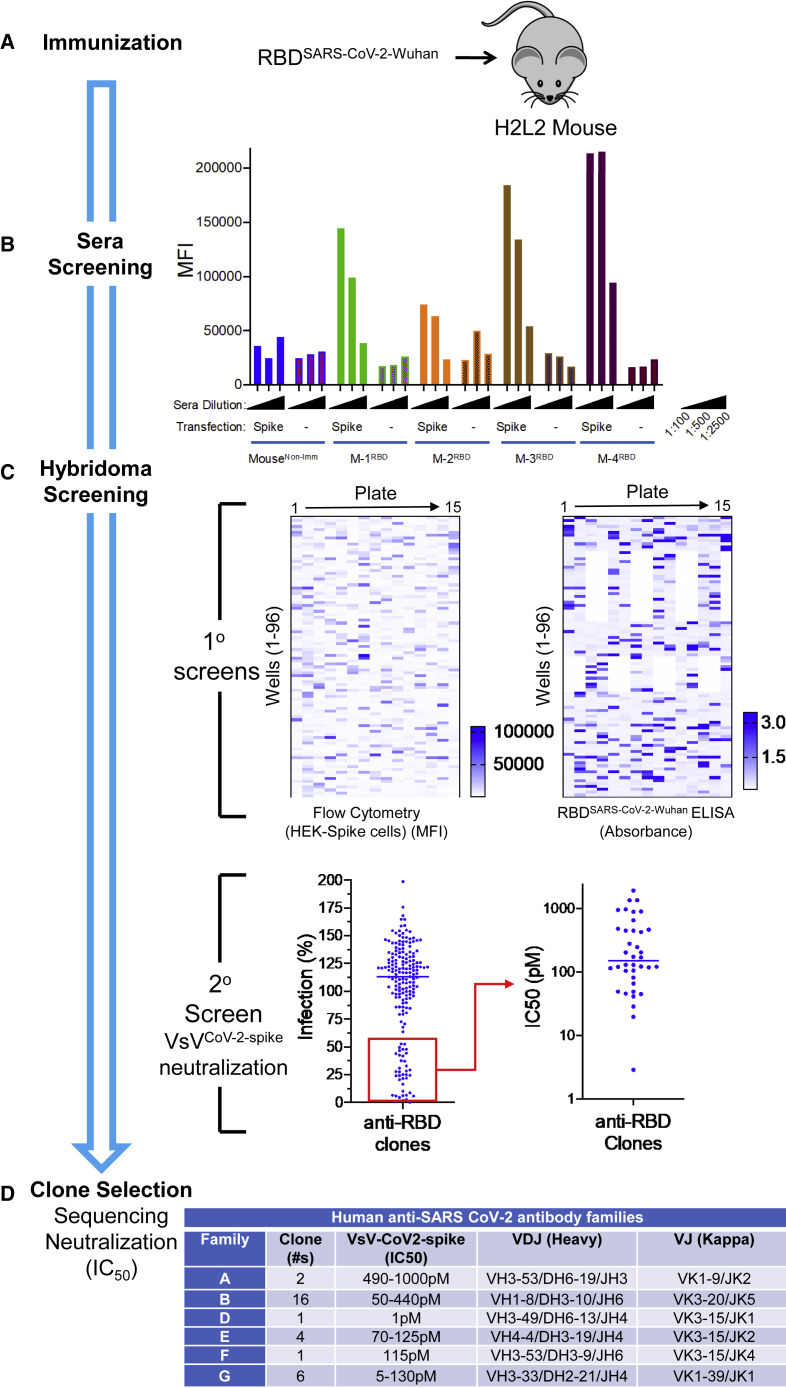
Figure 1.
Rapid discovery of neutralizing antibodies
(A and B) (A) Harbor H2L2 Mice (M-1, -2, -3, -4) were immunized and boosted 2× with SARS-CoV-2 RBD (Wuhan-1 strain) and (B) sera (1:100, 1:500, and 1:2,500) from these mice were analyzed by flow cytometry from Expi293F untransfected or transfected with the SARS-CoV-2 spike. As a control, serum from a non-immunized mouse was used.
(C) Primary screens based on the anti-RBD clones from mouse 4 (M-4) were performed using flow cytometry using HEK293 cells transfected with spike protein and RBD ELISA. Upon flow cytometry analysis, the MFI was determined for each clone. The RBD ELISA represents binding of the clones to RBD as measured by absorbance. Both the flow cytometry and ELISA data are represented as heatmaps. The secondary assays for the binding clones were a neutralization assay using VSV-spikeCoV−2 followed by a determination of IC50 (pM) for clones with >50% neutralization activity.
(D) The clones with IC50 values <500 pM were sequenced and mAb clones were identified by specific V(D)J gene-segment combinations and junction (CDR3) characteristics, which allowed them to be grouped into different clonal families (family “A-B &D-G”).