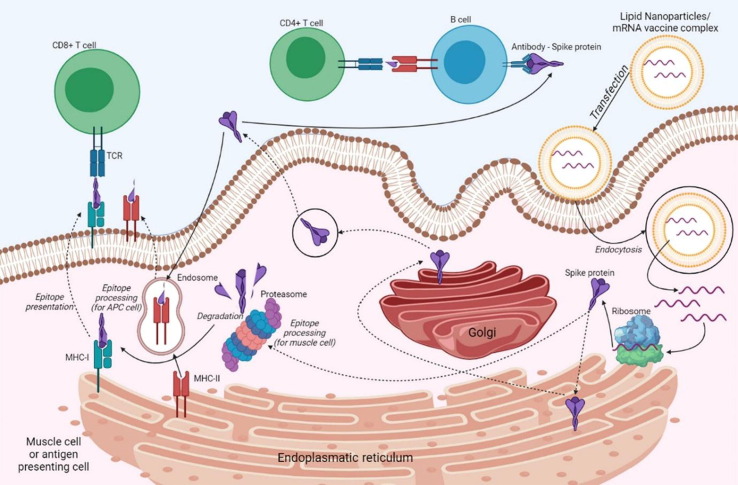
Fig. 3.
Immunogenic mechanism of mRNA vaccines. Through endocytosis, the vaccine enters a muscle cell or an antigen-presenting cell. LNP-free mRNA is translated into Spike protein at the ribosome level. The newly synthesized S protein is secreted into the extracellular space [cit] and through endocytosis enters an APC cell and is incorporated as part of the MHC-II to present the antigen to immune T and B cells. Protein antigens partially degraded by the proteasome are incorporated into MHC-I complexes and presented to immune cells. Created with BioRender.com.