Fig. 1. Diagram of using nanoparticles to therapeutically targets monocytes and macrophages in common CVDs.
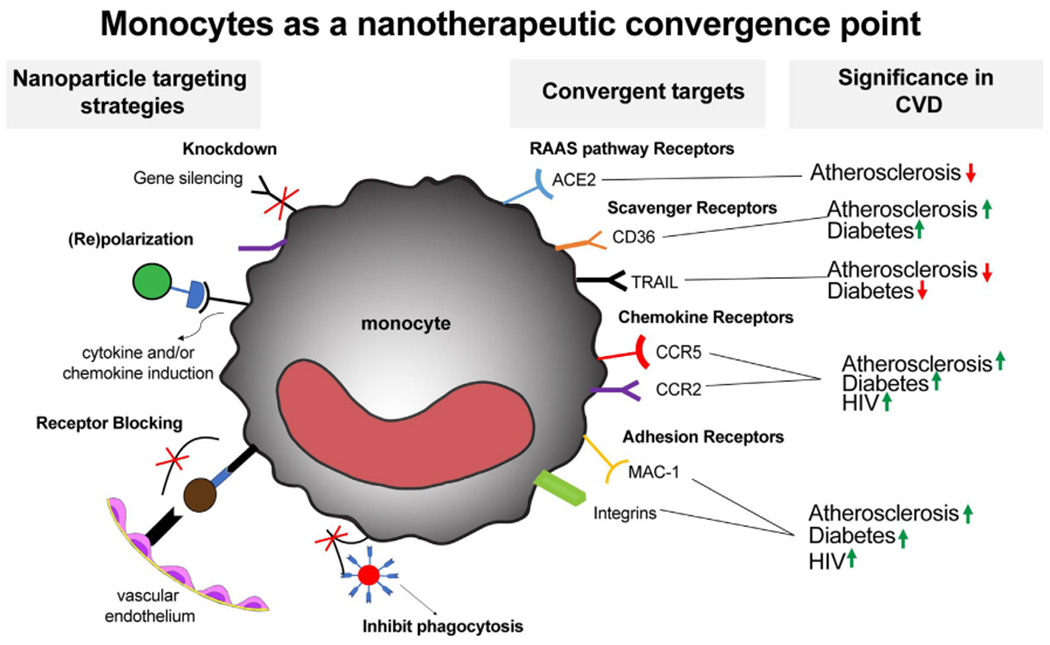
Nanoparticle targeting strategies highlight several themes in which nanoparticles can be used to change monocyte and macrophage function. (Knockdown) siRNA Delivery can used to decrease knockdown functionally relevant proteins. Re(polarization) Nanoparticles be used to change and/or maintain a given phenotype via cytokines or chemokines delivery. (Receptor Blocking) This tactic can be used to block receptor binding thereby inhibiting monocyte adhesion or transmigration into inflamed tissue. In addition, nanoparticles can be used to modulate phagocytosis to prevent bacterial or viral infection. These delivery strategies can be applied to various surface receptor classes on monocytes and macrophages. These receptors are often upregulated in CVDs and as such demonstrate the potential for these cells as convergent therapeutic targets. The arrows indicate whether the receptor is upregulated or downregulated in the disease.
