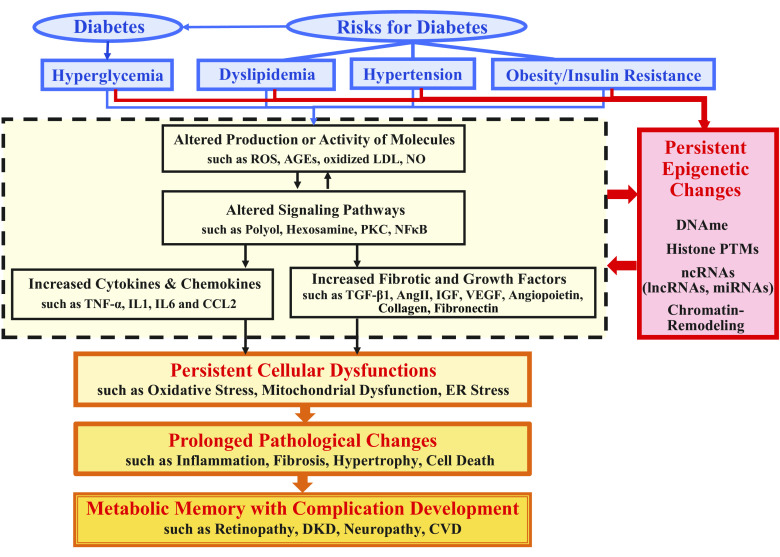
Figure 1.
Mediators of diabetic complications, involvement of epigenetic mechanisms and their persistence in metabolic memory. Hyperglycemia in diabetes or risk factors associated with diabetes such as obesity/insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and hypertension alter the production or activity of multiple molecules including ROS, AGEs, oxidized LDL, and NO, activate signaling pathways such as the polyol, hexosamine, PKC, and NF-κB, and subsequently induce proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL1, and IL6), chemokines (e.g., CCL2), and various disease/cell-specific growth and fibrotic factors such as TGF-β1, AngII, IGF, VEGF, angiopoietins, collagens, and fibronectin. These diabetic stimuli, especially hyperglycemia, and the indicated subsequent downstream effects can also induce epigenetic changes including DNAme, histone PTMs, chromatin-remodeling, along with ncRNAs (lncRNAs and miRNAs) that can act via epigenetic mechanisms. Persistence of some of these changes even after glucose levels are normalized can cause long-term persistent cellular malfunction including mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and ER stress. This results in prolonged pathological changes such as inflammation with monocyte/macrophage infiltration, fibrosis with extracellular matrix accumulation, hypertrophy, and cell death (apoptosis) in diabetes-targeted cells/tissues/organs, leading to development and/or uncontrolled progression of complications including retinopathy, DKD, neuropathy, and CVD, sometimes even after glycemic control. AGE, advanced glycation end product; AngII, angiotensin II; CCL2-C, C motif chemokine ligand 2; CVD, cardiovascular disease; DKD, diabetic kidney disease; DNAme, DNA methylation; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; histone PTM, histone posttranslational modification; IGF, insulin-like growth factor; IL1, interleukin 1; IL6-interleukin 6; LDL, low density lipoprotein; lncRNA, long noncoding RNA; miRNA, microRNAs; ncRNA, noncoding RNA; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; NO, nitric oxide; PKC, protein kinase C; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TGF-β1, transforming growth factor β1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.