Figure 2.
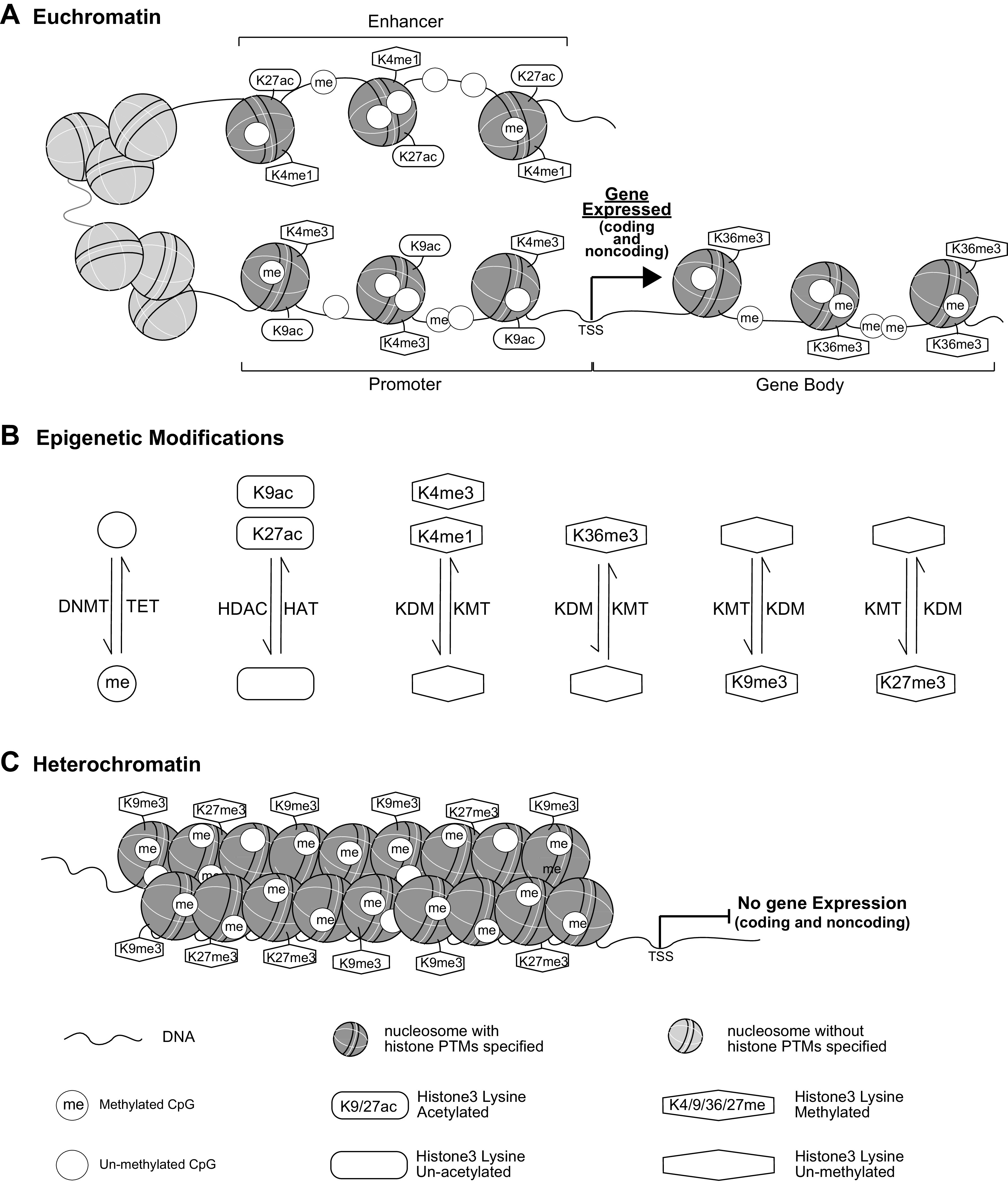
Epigenetic regulation of gene expression. Key epigenetic marks, including DNAme and histone PTMs, associated with euchromatin and heterochromatin are shown in A and C, respectively, and the interconversions between these two chromatin structures are shown in B. DNAme and histone PTMs interface with chromatin remodeling complexes, and noncoding (nc) RNAs to remodel chromatin into two major chromatin states, euchromatin and heterochromatin. At euchromatin (A) where loosely packed nucleosomes allow open chromatin states more easily accessible to transcription factors and RNA polymerases, gene promoters are usually enriched with marks such as histone H3K4me3 and H3K9ac, enhancers with H3K4me1 and H3K27ac, and gene bodies with H3K36me3. DNAme levels are low at enhancers and promoters, and high in gene bodies. With the binding of transcription factors to enhancers and promoters in euchromatin, RNA polymerases are recruited to either coding or noncoding (including pri-miRNAs and lncRNAs) genes for active transcription. Pri-miRNAs are processed to mature miRNAs via posttranscriptional processes in the cytoplasm, and lncRNA can modulate chromatin functions by interaction with chromatin factors, RNA binding proteins, and enhancers (not shown). On the other hand, nucleosomes at heterochromatin (C) are densely packed and the associated epigenetic marks include H3K9me3, H3K27me3 and DNAme. With reduced accessibility to transcription factors and RNAs polymerases at heterochromatin regions, gene transcription/expression is inhibited. The signals of each epigenetic mark enriched at euchromatin or heterochromatin regions can be modified by the dynamic actions of writers or erases, including histone and DNA methyltransferases, histone acetyltransferases, demethylases, and deactylases (shown in B) allowing for the remodeling of chromatin structure. TSS, transcription start site; DNMT, DNA methyltransferase; HAT, histone acetyltransferase; HDAC, histone deacetylase; KDM, histone lysine demethylase; KMT, histone lysine methyltransferase; PTMs, posttranslational modifications; TET, ten-eleven translocation enzyme.
