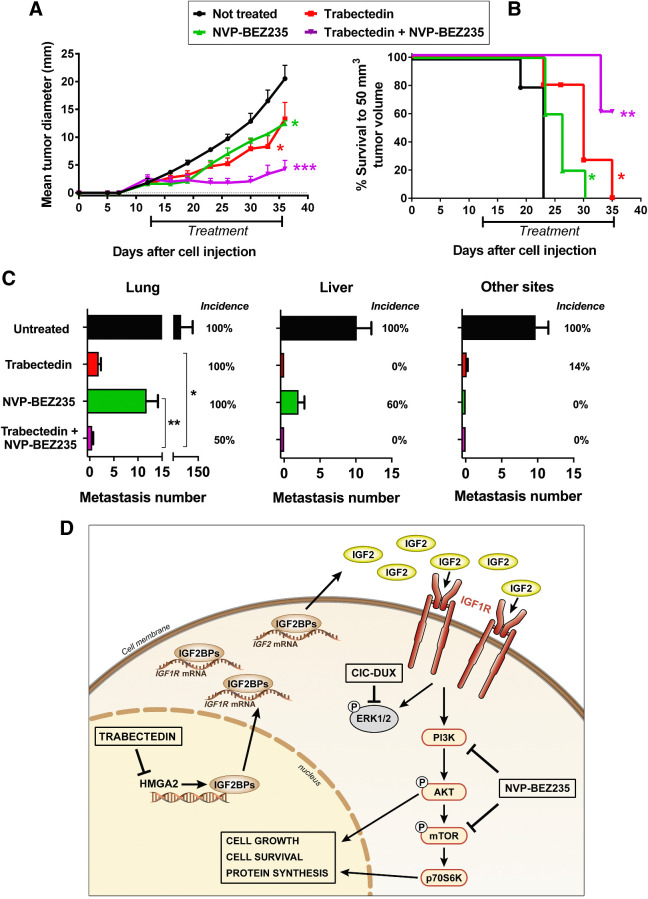
Figure 5.
Efficacy of combined treatment with trabectedin and NVP-BEZ235 against CDS tumor growth and metastasis and schematic representation of the CDS-specific HMGA2/IGF2BPs/IGF2/IGF1R/AKT-mTOR pathway. A, Inhibition of PDX-CDS #4-C tumor growth after treatments with trabectedin and/or NVP-BEZ235. Significant reduction in tumor growth was observed after single treatments (*, P < 0.05, Student t test) but the inhibition increased after combination of the two drugs (significance was at least ***, P < 0.001, Student t test starting from day 23) or to single treatments (*, P < 0.05). Points, tumor diameter means (calculated as geometric mean in mm); bars, SE. Drugs were administered as indicated in the Supplementary Material and Methods. B, Tumor-free survival curves of mice treated with trabectedin and/or NVP-BEZ235. Kaplan–Meier curves and Mantel–Cox tests (compared with untreated mice) are shown: *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01. C, Inhibition of PDX-CDS#4-C experimental metastases to the lungs, liver, and other sites (mainly interscapular adipose tissue and lymph nodes) after treatments with trabectedin and/or NVP-BEZ235, starting from 7 days after intravenous cell injection. All of the treated groups developed a significantly lower number of metastases than untreated mice by the nonparametric Mann–Whitney test (P < 0.01; n = 7 for untreated control group and trabectedin; n = 5 for NVP-BEZ235; n = 6 for the combination Trabectedin + NVP-BEZ235). In the lung, the combined treatment led to a significant lower number of metastases compared with trabectedin (*, P < 0.05), or with NVP-BEZ235 (**, P < 0.01) as single agents. Bars, metastasis number means and SE. Incidence of mice with metastasis to the different sites (mice with metastasis/total number of mice per group) is reported as percentage. D, In the nucleus, high expression of HMGA2 favors the transcription of IGF2BP2 and IGF2BP3. In the cytoplasm, IGF2BP2 and IGF2BP3 directly bind to and stabilize IGF2 and IGF1R mRNAs, which subsequently activate IGF1R signaling. The repression of MAPK signaling by the CIC-DUX4 fusion protein renders CDSs mainly dependent on the AKT/mTOR pathway. Trabectedin can impair HMGA2 activity by preventing its binding to promoters, thus inhibiting the transcription of its targets IGF2BP2 and IGF2BP3 and decreasing IGF2/IGF1R signaling. NVP-BEZ235 is a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor used in phase II clinical trials. The combination of trabectedin with NVP-BEZ235 synergistically inhibits tumor growth.