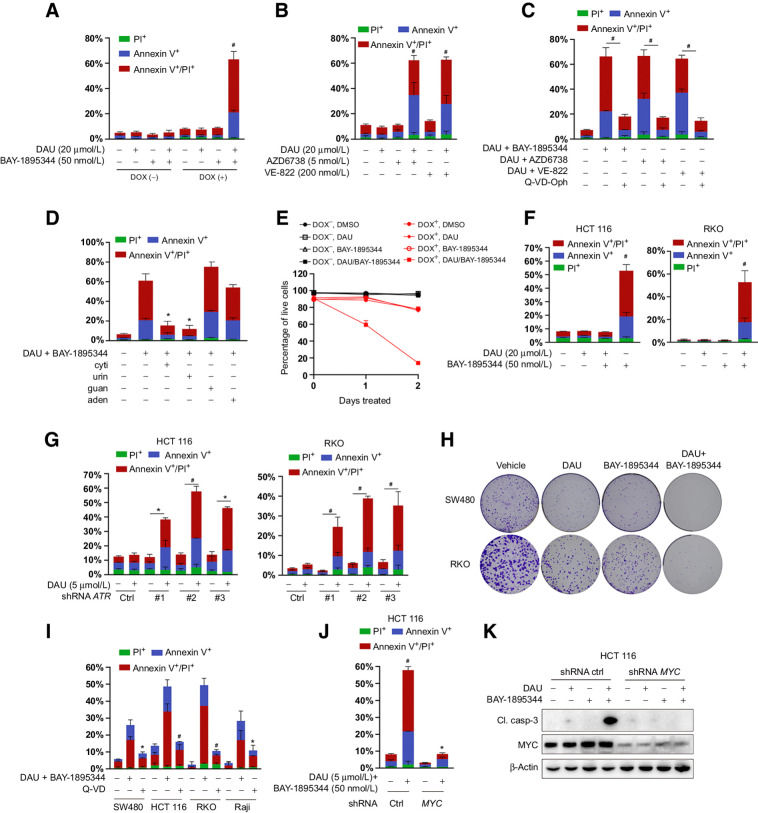
Figure 4.
Combined inactivation of CTPS and ATR is synthetically lethal to MYC-transformed cells. A, Apoptosis analysis of ARPE-19-MYC (DOX+) and ARPE-19-MYC (DOX−) cells treated with DAU and BAY-1895344 alone or together for 24 hours. B, Apoptosis analysis of ARPE-19-MYC (DOX+) cells treated with DAU alone or together with AZD6738 or VE-822 for 24 hours. C, The impacts of Q-VD-Oph on the combination of DAU and ATR inhibitor-induced apoptosis in ARPE-19-MYC (DOX+) cells. #, P < 0.001. D, Apoptosis analysis of ARPE-19-MYC (doxycycline+) cells treated with DAU (20 μmol/L)/BAY-1895344 (50 nmol/L) with or without 50 μmol/L cytidine (cyti), uridine (urid), guanosine (guan), or adenosine (aden) for 24 hours. E, Cell death analysis of ARPE-19-MYC (doxycycline+) and ARPE-19-MYC (doxycycline−) cells treated with DAU (20 μmol/L) and BAY-1895344 (50 nmol/L) alone or together for the indicated time. F, Apoptosis analysis of the indicated cells treated with DAU and BAY-1895344 alone or together for 48 hours. G, HCT116 and RKO cells expressing control or ATR shRNA were treated with DAU for 48 hours, followed by apoptosis analysis. *, P < 0.01; #, P < 0.001. H, Effect of DAU and BAY-1895344 on clonogenic survival of SW480 and RKO cells. I, The impacts of Q-VD-Oph on the combination of DAU- and BAY-1895344–induced apoptosis in the indicated cells. J and K, Control and MYC knockdown HCT116 cells were treated with DAU and BAY-1895344 for 48 hours, followed by Annexin V/PI–based apoptosis analysis (J) and immunoblotting analysis (K). Graphical data are means ± SEM. n = 3–4. For A, B, F, and J, *, P < 0.05; #, P < 0.0001; significantly different from DMSO-treated group. For D and I, *, P < 0.01; #, P < 0.0001; significantly different from DAU/BAY-1895344–treated group. DOX, doxycycline; ctrl, control; Cl. casp-3; cleaved caspase-3.