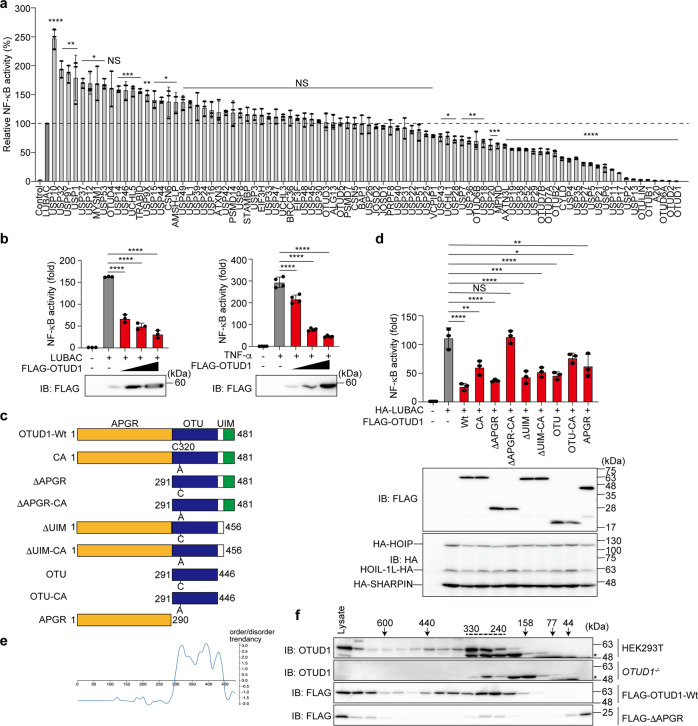
Fig. 1. OTUD1 suppresses canonical NF-κB activation through the catalytic activity and the N-terminal region.
a Screening for DUBs that regulate LUBAC-mediated NF-κB activation. Effects of 88 human DUBs on LUBAC-induced NF-κB activation were analyzed by a luciferase assay. b Dose-dependent inhibition by OTUD1 on LUBAC- and TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation. Effects of increasing amounts (0.1, 0.3, and 1.0 μg) of OTUD1 were examined with co-expression of LUBAC or 6 h treatment with 10 ng/ml TNF-α in HEK293T cells. c Domain structure of wild-type (Wt) and mutants of OTUD1. APGR: Ala-, Pro-, and Gly-rich region; OTU ovarian tumor protease, UIM ubiquitin-interacting motif. d Effect of OTUD1 mutants on the LUBAC-induced NF-κB activity. The relative NF-κB activity induced in the presence of Wt or various mutants of OTUD1, and expression levels of OTUD1 and LUBAC subunits are shown. a, b, d Data are shown as mean ± SD by ANOVA post-hoc Tukey test (n = 3 or 4). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, NS not significant. e The N-terminal APGR region is disordered. Intrinsically ordered and disordered segments of OTUD1 were analyzed by DICHOT [12] (https://idp1.force.cs.is.nagoya-u.ac.jp/dichot/). f OTUD1 eluted in the high molecular weight fractions. Gel filtration analyses of lysates prepared from parental and OTUD1−/− cells, and FLAG-OTUD1-Wt- and FLAG-ΔAPGR-expressing HEK293T cells were performed using a Superdex 200 column. Concentrated fractions were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. *Non-specific signal.