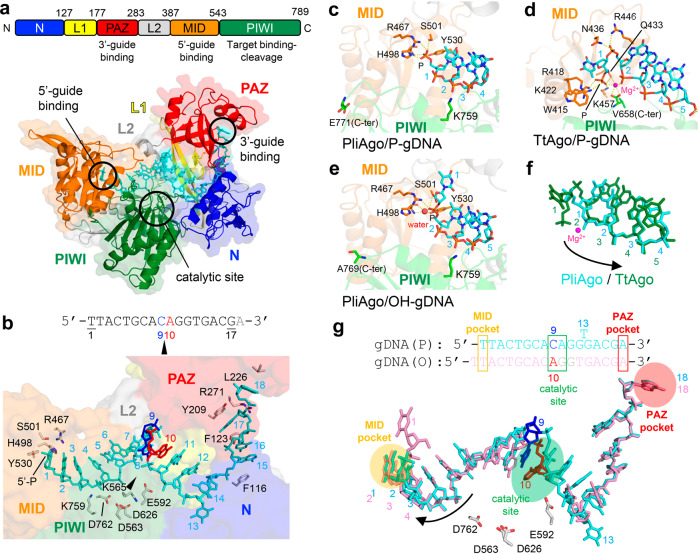
Fig. 2. Structure of PliAgo and its interactions with guide DNA.
a The structure of the PliAgo and P-gDNA complex. (Top) The primary structure of PliAgo with amino acid numbering. Domains and their functions are colored and labeled. (Bottom) Overall structure of the PliAgo-P-gDNA complex. PliAgo and DNA are depicted as ribbon and stick models, respectively, with partially transparent surfaces. Domains are colored as in the top panel and labeled. b The PliAgo and P-gDNA interactions. (Top) The guide DNA sequence used for complex crystallization. Nucleotides that define the site of target RNA cleavage are colored. (Bottom) A magnified view of the PliAgo-P-gDNA interactions. PliAgo is depicted as a partially transparent surface. DNA nucleotides and amino acid residues responsible for guide positioning are shown as stick models and labeled. The catalytic site is indicated as a black triangle. The view is the same as a. c–e The guide 5’-end binding in the PliAgo-P-gDNA complex c TtAgo-P-gDNA complex (PDB: 3DLH32) d, and PliAgo-OH-gDNA complex e. PliAgo and TtAgo are depicted as partially transparent ribbon models. Amino acid residues responsible for 5’-end binding are shown as stick models and labeled. Salt bridges between amino acid residues and phosphate groups as well as coordination bonds of Mg2+/water are shown as yellow dashed lines. f Overlay of guide DNAs in the PliAgo-P-gDNA (cyan) and TtAgo-P-gDNA complexes (green). Positions of guide DNA nucleotides are labeled. Shifting the register of guide DNA from TtAgo to PliAgo is indicated by a black arrow. g 5’-phosphate dependent guide DNA positioning by PliAgo. (Top) The registers of 5’-P and 5’-OH guide DNAs in the PliAgo-gDNA complexes. (Bottom) Overlay of the guide DNA in the complexes of PliAgo with P-gDNA (cyan) and OH-gDNA (pink). Shifting the register of guide DNA without the 5’-phosphate group is indicated by a black arrow.