Table 3.
Examples of small molecules that bind to RNAs implicated in neuromuscular and neurodegenerative diseases
| Compound/institution | Associated disease | RNA target | Mode of action | Stage of development | Activity | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
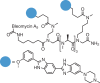
Cugamycin/Scripps Research Institute |
Myotonic dystrophy type 1 | r(CUG)exp in DMPK mRNA | Displaces MBNL1 from binding to r(CUG)exp | Early discovery | Kd = 365 nM (for r(CUG)12); EC25 = 840 nM (rescued splicing defects) | 278 |
|
Synucleozid/Scripps Research Institute |
Parkinson disease | Iron-responsive element in α-synuclein mRNA | Inhibits ribosomal assembly and polysome loading onto α-synuclein mRNA | Early discovery | Kd = 1.5 μM; IC50 (neurons) = 0.5 μM | 13 |
|
Mitoxantrone/University of Washington, Seattle |
Alzheimer disease; frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism-17 | Exon 10–intron junction in MAPT pre-mRNA | Inhibits binding of splicing machinery at the exon 10–intron junction; also inhibits a fungal group II intron277 | Early discovery | Kd <1 μM; EC50 = 700 nM (competition of binding with 25 nM pyrene–neomycin conjugate) | 225,279 |
|
Compound 9/Scripps Research Institute |
Alzheimer disease; frontotemporal dementia with parkinsonism-17 | Exon 10–intron junction in MAPT pre-mRNA | Inhibits binding of splicing machinery at the exon 10–intron junction | Early discovery | Kd = 4.9 μM; IC50 (transfected HeLa cells) = 10 μM; decreased 4R/3R ratio by ~50% in primary neurons at 40 μM | 70,228 |
|
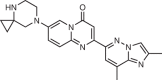
Risdiplam/Roche and PTC Therapeutics |
SMA | SMN2 pre-mRNA exon 7–intron junction | Promotes exon inclusion by stabilizing the binding of the splicing machinery | FDA approved | Kd = 15 nM; EC1.5x (SMA patient-derived fibroblasts) = 7 nM | 14 |
|
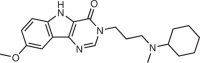
Branaplam |
SMA; HD | SMN2 pre-mRNA exon 7–intron junction | Promotes exon inclusion by stabilizing the binding of the splicing machinery | Phase I/II clinical trial (for SMA: NCT02268552; for HD: NCT05111249) | EC50 (SMN ELISA in SMNΔ7 mouse myoblasts) = 20 nM | 15 |
EC50, half maximal effective concentration; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; HD, Huntington disease; IC50, half maximal inhibitory concentration; Kd, dissociation constant; SMA, spinal muscular atrophy; SMN, survival of motor neuron.