Fig. 8.
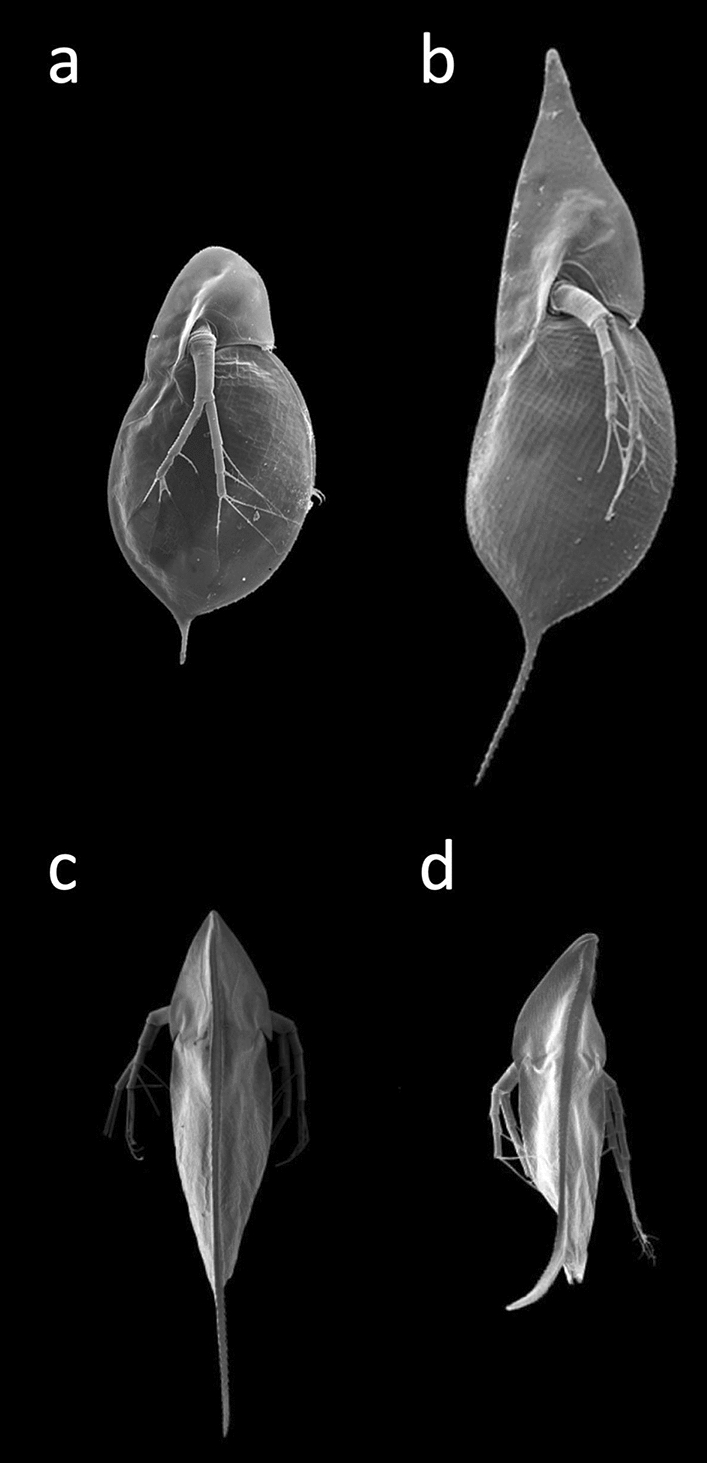
Waterfleas are able to react to cues from the environment, including water turbulences and infochemicals (kairomones) released by different predators, with the formation of highly specific structures, such as protective tail spines, helmets, and neck teeth. a D. cucullata in its normal (uninduced) phenotype (left) and b after induction (right). Helmets can be induced by water turbulence and by kairomones from fish. [81, 132]. c D. barbata: left control, d right induced by kairomones released by the predatory tadpole shrimp Triops cancriformis. The “twist”, a body torsion, induced by the kairomones reduces the likelihood of predation by Triops [75]. Pictures by Christian Laforsch, University of Bayreuth, Germany
