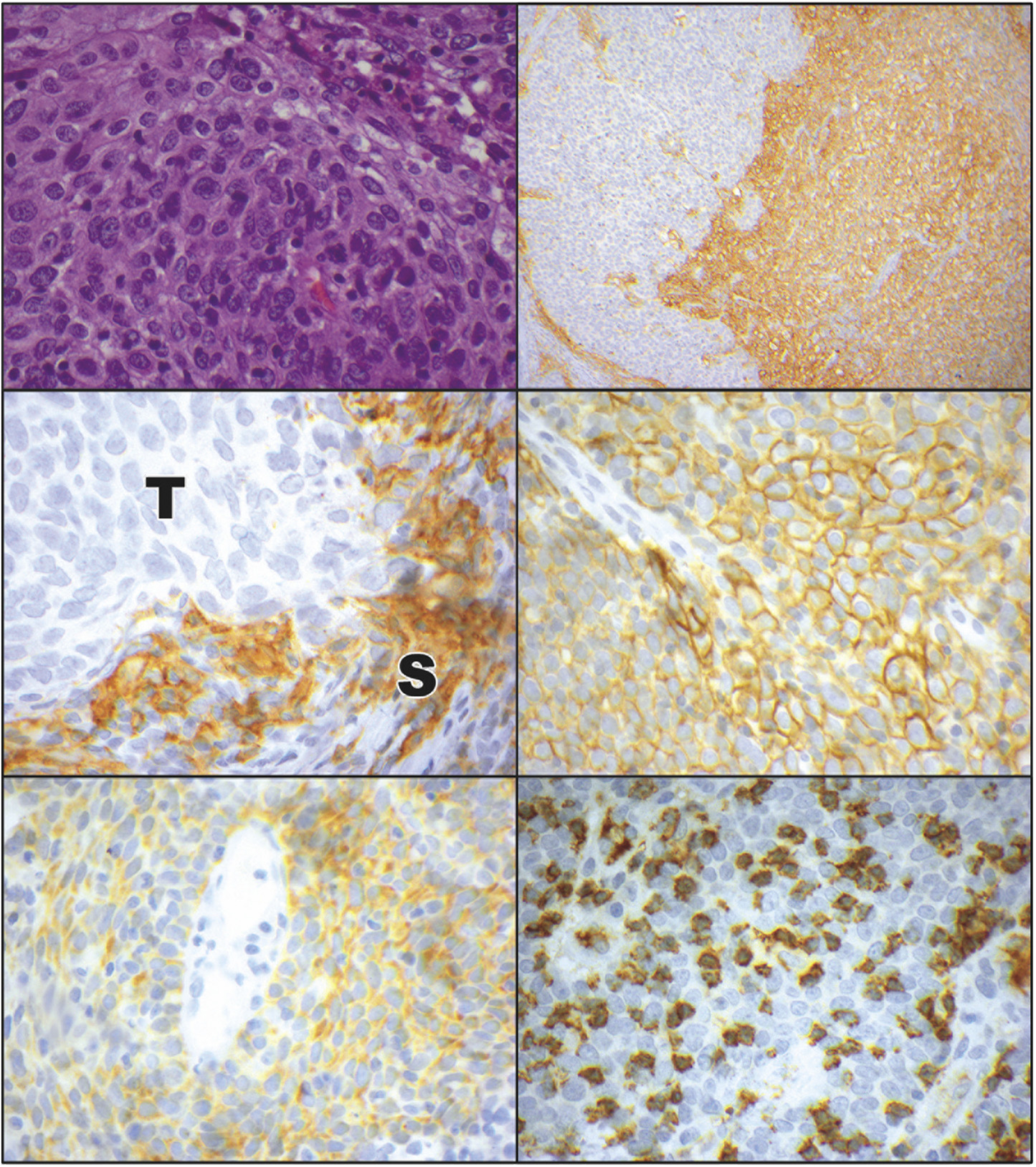
FIGURE 2. Programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1) and programmed cell death ligand 2 (PD-L2) expression in ocular adnexal sebaceous carcinoma. (Top left) Photomicrograph of ocular adnexal sebaceous carcinoma. These variably vacuolated tumors were heterogeneously positive for PD-L1 and PD-L2 (hematoxylin and eosin, ×40). (Top right) Immunostaining for PD-L1 revealed a heterogeneous pattern of positivity, with some areas of the tumor weakly staining (left side), while other areas had diffuse PD-L1 positivity (right side; immunoperoxidase reaction, diaminobenzidine chromogen, hematoxylin counterstain, ×10). (Middle left) Some tumors had a predominance of PD-L1 positivity in the stromal (S) cells, with an absence of immunostaining in the adjacent tumor (T) cells (immunoperoxidase reaction, diaminobenzidine chromogen, hematoxylin counterstain, ×60). (Middle right) Other tumors displayed a predominance of membranous PD-L1 immunostaining in the tumor cells (immunoperoxidase reaction, diaminobenzidine chromogen, hematoxylin counterstain, ×60). (Bottom left) PD-L2 positivity in a membranous pattern was manifested by the tumor cells. There was also positivity on some intermixed stromal cells (immunoperoxidase reaction, diaminobenzidine chromogen, hematoxylin counterstain, ×60). (Bottom right) Many sebaceous carcinomas had a heavy infiltrate of associated CD8-positive T-lymphocytes (immunoperoxidase reaction, diaminobenzidine chromogen, hematoxylin counterstain, ×60).