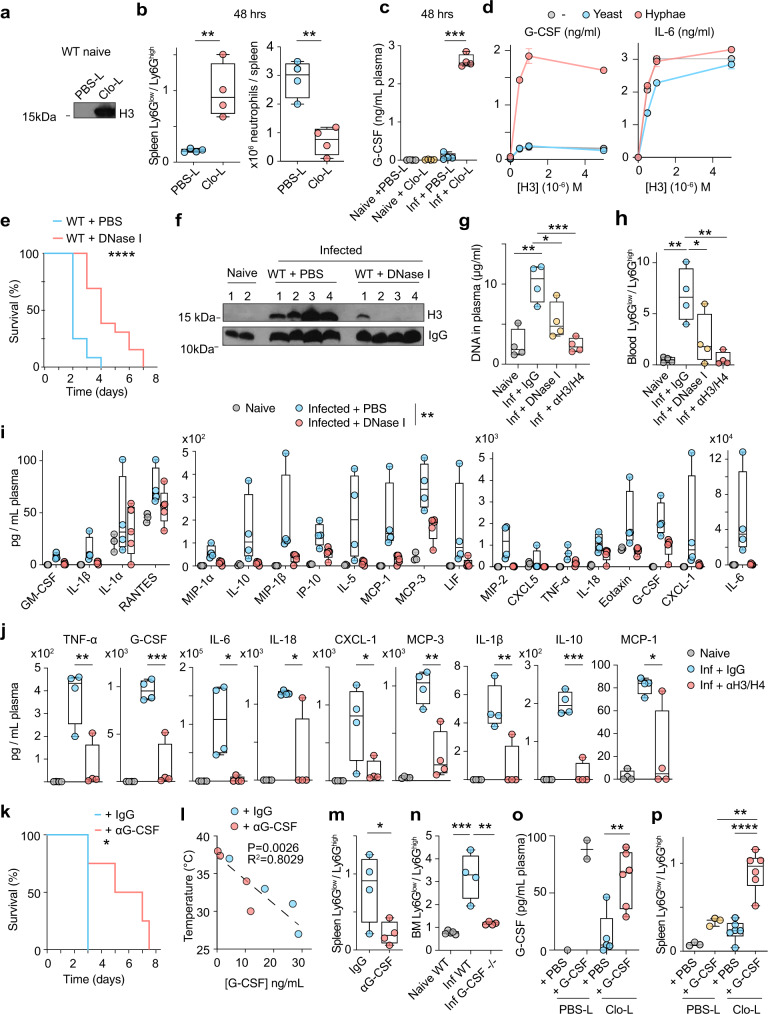
Fig. 7. Extracellular chromatin and G-CSF alter neutrophil populations.
a Western immunoblotting for plasma histone H3 in naïve WT mice 24 h after intravenous injection of PBS-liposomes (PBS-L) or clodronate-liposomes (Clo-L). b, c Ly6Glow/Ly6Ghigh ratios (left panel) and total neutrophils (right panel) in the spleens (b) and plasma G-CSF concentrations assessed by simplex immunoassay (c) from naïve or infected WT mice with 1 × 105 WT C. albicans, pre-treated with PBS-L or Clo-L, 48 h post-infection (n = 4 mice per group). Average and SD. d G-CSF (left) and IL-6 (right) protein production in WT BM-derived macrophages alone (grey) or in the presence of heat-inactivated yeast (blue) or hyphae (red) alone or in combination with increasing concentrations of recombinant histone H3. Average and SD from two technical replicates per condition. Representative of three independent experiments. e Survival of WT mice pre-treated with PBS (blue) or DNase I (red) and infected with 5 × 105 WT C. albicans. Representative of 3 individual experiments with 6 (PBS) and 12 (DNase I-treated) mice per group. f–j Histone H3 (f), DNA levels (g) neutrophil Ly6Glow/Ly6Ghigh ratios (h) and cytokines and chemokines (i, j) in the plasma of naïve or infected WT mice with 5 × 105 WT C. albicans, pre-treated with either IgG control antibody, anti-H3 and anti-H4 antibodies, or DNase I, analysed 72 h post-infection (naïve n = 3 and infected n = 5 mice per group and two independent experiments). k Survival of WT mice infected with 5 × 105 WT C. albicans and treated daily with control (blue) or anti-G-CSF (red) antibodies starting at 24 h post-infection (n = 4 mice per group and two independent experiments). l, m Correlation between plasma G-CSF concentrations and body temperature (l) and Ly6Glow/Ly6Ghigh ratios in splenic neutrophils (m) at 72 h post-infection in infected WT mice treated with control (blue) or anti-G-CSF antibody (red) (n = 4 mice per group). n Ly6Glow/Ly6Ghigh BM neutrophil ratio from naïve WT and G-CSF-deficient FVB/NJ mice or infected with 1 × 104 or 1 × 103 WT C. albicans respectively, 72 h post-infection (n = 4 mice per condition and two independent experiments). o, p Plasma G-CSF concentrations (o) and Ly6Glow/Ly6Ghigh ratios (p) in splenic neutrophils from naïve mice treated with PBS-L or Clo-L, subsequently injected with PBS or recombinant G-CSF (rG-CSF) after 24 h and assessed 48 h later (PBS-L n = 3 and Clo-L n = 6 (Clo-L) mice per group, representative of two experiments). Panel: LD Blue, CD3/CD19 PerCP-Cy5.5, CD11b-PECy7, Ly6G-APC. Statistical analysis by unpaired two-sided Mann–Whitney t-test for single comparison, two-sided Log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test for survival analysis and two-way Anova for cytokine array with multiple comparisons (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001).