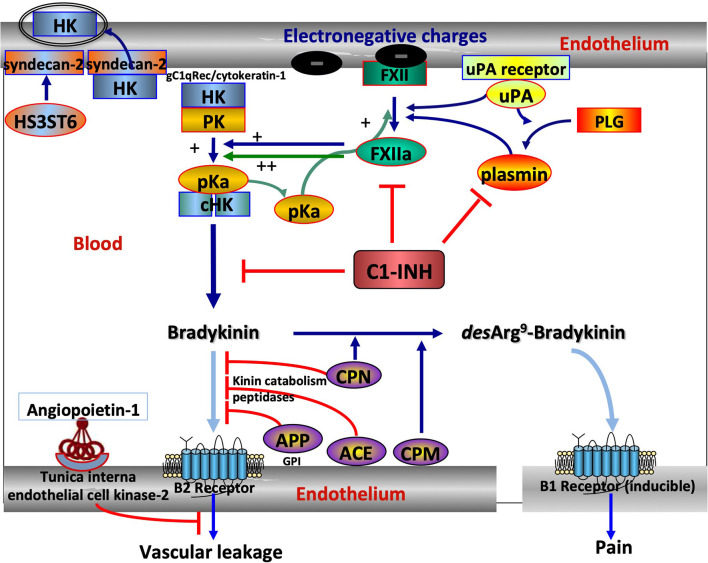
Figure 1.
The central position of C1 Inhibitor (C1-INH) within the kallikrein–kinin system (KKS) and its companions. KKS activation is triggered when FXII becomes activated into FXIIa on binding to an activator onto an electronegative membrane. KKS activation results in HK cHK and bradykinin (BK). The serpin C1-INH controls both activation and activity of KKS, with zymogen to enzyme conversion of FXII and pK. C1-INH also controls the reciprocal activation of FXII and pK by plasmin in an interconnected amplification (5). ANGPT1 is a secreted protein ligand for tunica interna endothelium kinase-2, a receptor expressed in growing vascular endothelial cells. ANGPT1 targets key mechanisms contributing to the maintenance of endothelium function by inhibiting the effects of permeability enhancing agents, including BK, protecting from extensive permeability. H3ST6 is involved in HK docking on the endothelial cell surface, preventing HK binding to gC1q receptor and cytokeratin-1 and engaging in kinin forming. Aminopeptidase P (APP) and Angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) are the membrane peptidases that inactivate BK, whereas carboxypeptidases M and N transform a B2 ligand into a B1 ligand. What this scheme means for understanding hereditary angioedema (HAE). SERPING1 variants display a markedly reduced control function of C1-INH toward KKS and plasmin. F12 and PLG variants are shown to increase FXII and plasminogen (PLG) activation, respectively, and KNG1 variants more susceptible to HK cleavage with BK production. ANGPT1 variants showed reduced capacity to bind its natural receptor, with less control of BK-dependent vascular leakage. Because of incomplete heparan-sulfate modification of syndecan-2 by H3ST6, H3ST6 variants were less able to take up HK via endocytosis into the endothelial cell and more HKs entering into the KKS process. Dark blue arrows indicate activation, green arrows the amplification loop, light blue arrows the ligand–receptor interactions, and red lines indicate an inactivation of BK function. FXII, Factor XII; pK, prekallikrein; pKa, plasma kallikrein; HK, High-molecular-weight kininogen; cHK, cleaved HK; ANGPT1, angiopoietin-1; H3ST6, Heparan-sulfate-glucosamine 3-O-sulfotransferase 6; uPA, urokinase-type plasminogen activator.