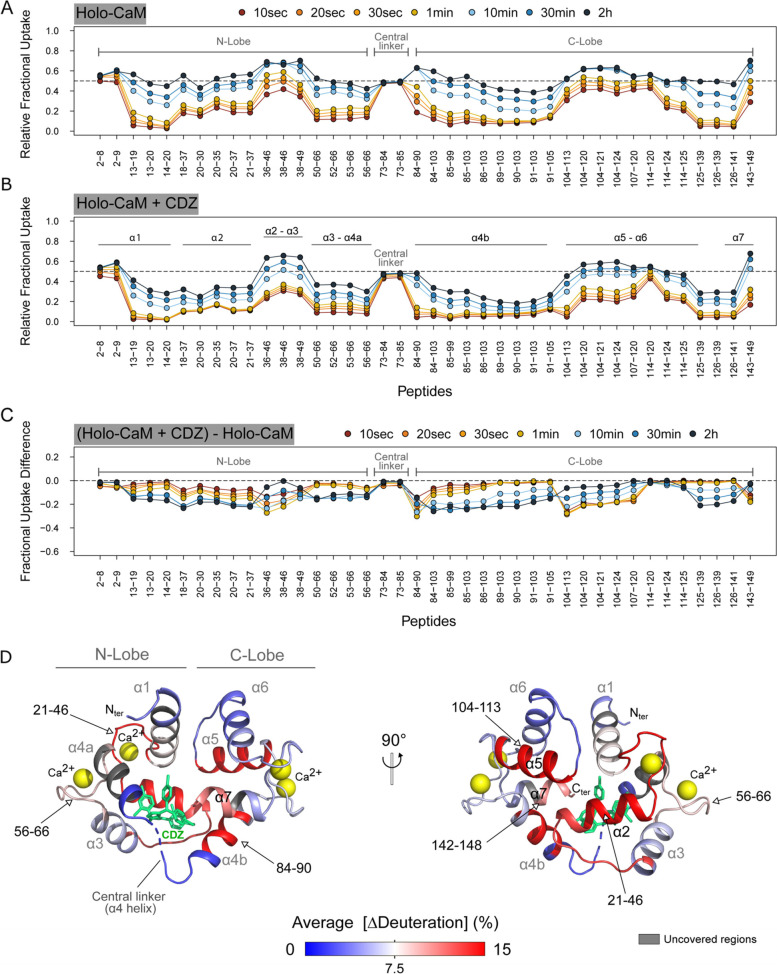
Fig. 3.
Effects of CDZ binding on the deuterium uptake profile of holo-CaM. A, B Relative fractional uptake plots of holo-CaM measured in the presence and in the absence of 20 μM CDZ. Each dot corresponds to the average uptake value measured in three independent replicates. C The effects of CDZ binding on holo-CaM are visualized on the fractional uptake difference plot. Negative values indicate a reduction in solvent accessibility induced by CDZ binding. D Cartoon representation of holo-CaM showing the average differences in “fractional uptake differences” between the CDZ-bound and free holo-CaM states. The fractional uptake differences ([ΔDeuteration] in %) measured between the CDZ-bound and free states were extracted for each peptide at each labelling time point, averaged, and plotted on the crystal structure of CaM:CDZA (PDB ID: 7PSZ). CDZ-A is colored in green. The average ΔDeuteration values [Average (ΔDeuteration)] are colored from blue (no variation) to red (major reductions in uptake)