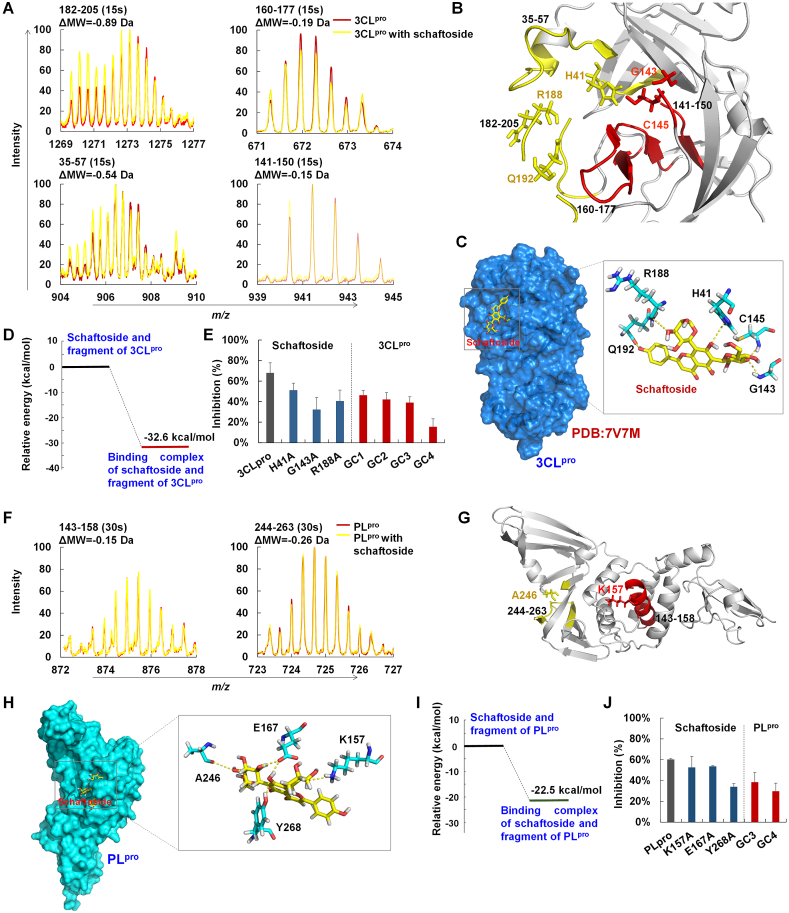
Figure 3.
Binding mechanisms of schaftoside with 3CLpro and PLpro. (A) Mass spectra of peptides 182–205 and 35–57 (15 s) of 3CLpro and 3CLpro with schaftoside determined by hydrogen–deuterium exchange mass spectrometry (HDX-MS). (B) Location of peptides 35–57, 182–205, and 141–150 in 3CLpro. (C) The crystal structure of 3CLpro (PDB ID: 7V7M), and the binding mode of schaftoside with active residues of 3CLpro by molecular docking. Hydrogen bonds (yellow dashes) are formed between schaftoside and residues H41, R188, Q192, G143 and C145 of 3CLpro. (D) Relative energy of schaftoside with 3CLpro computed by quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM). (E) Inhibitory activities of schaftoside (8 μmol/L) against SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro and 3CLpro mutants, and of flavonoid C-glycosides GC1, GC2, GC3 and GC4 (8 μmol/L) against SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro. SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro and 3CLpro mutants were expressed and purified by our laboratory. (F) Mass spectra of peptides 143–158 and 244–263 (15 s) of PLpro and PLpro treated with schaftoside determined by HDX-MS. (G) Location of peptides 143–158 and 244–263 in PLpro. (H) Binding mode of schaftoside with active residues of PLpro by molecular docking. Hydrogen bonds (yellow dashes) are formed between schaftoside and residues K157, E167, A246 and Y268 of 3CLpro. (I) Relative energy of schaftoside with PLpro computed by QM/MM. (J) Inhibitory activities of schaftoside (8 μmol/L) against SARS-CoV-2 PLpro and PLpro mutants, and of flavonoid C-glycosides GC3 and GC4 (8 μmol/L) against SARS-CoV-2 PLpro.