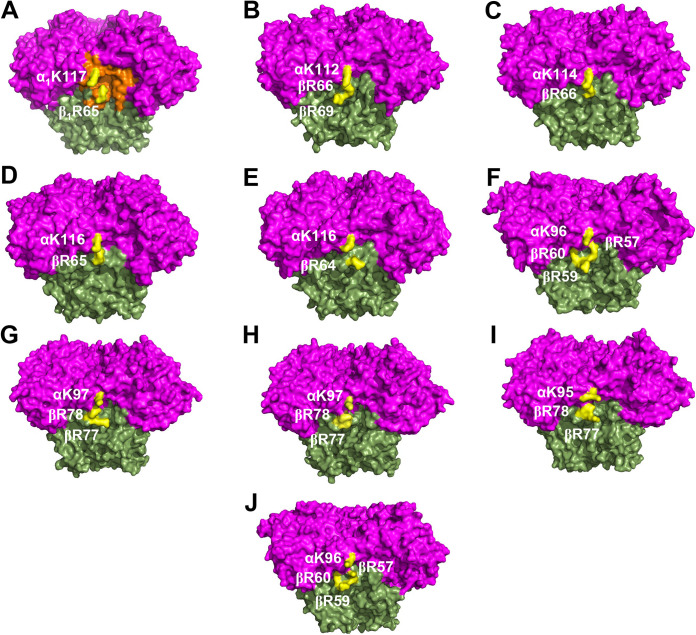
FIG 4.
Conserved charged residues in the structures of α3β3-type Oxy components. Structures of different α3β3-type Oxys of 10 RO systems are shown: (A) CumDO from P. fluorescens IP01 (PDB entry 1WQL), (B) TDO from P. putida F1 (PDB entry 3EN1), (C) BDO from R. jostii RHA1 (PDB entry 1ULI), (D) BDO from P. pnomenusa B-356 (PDB entry 3GZY), (E) BDO from B. xenovorans LB400 (PDB entry 2XR8), (F) BDO from Sphingomonas yanoikuyae B1 (PDB entry 2GBX), (G) NDO from Pseudomonas sp. strain NCIB9816-4 (PDB entry 1NDO), (H) NDO from Pseudomonas sp. strain C18 (PDB entry 4HJL), (I) NBDO from Comamonas sp. strain JS765 (PDB entry 2BMO), and (J) PAH-hydroxylating dioxygenase from Sphingomonas sp. strain CHY-1 (PDB entry 2CKF) are shown in the side view. α- and β-subunits are shown in magenta and green, respectively. The groove of the potential CumDO-F binding site is shown in orange in panel A. Conserved positive-charged residues are in yellow.