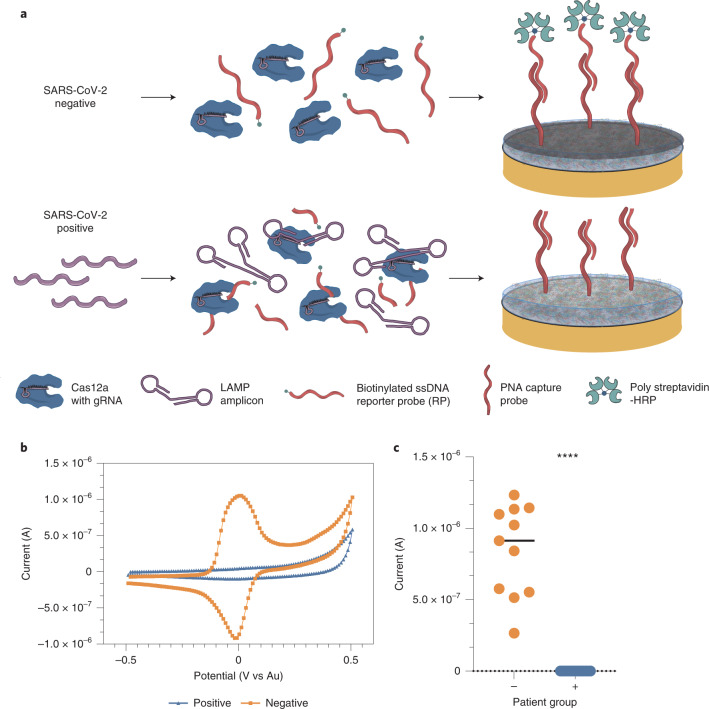
Fig. 2. Schematic of the CRISPR electrochemical assays and assay performance using clinical samples.
a, Schematic illustrating the surface chemistry of the EC assay. Without viral RNA (top row), the biotinylated ssDNA RP probe is not cleaved; therefore, the polystreptavidin-HRP binds to the PNA/biotin-DNA duplex when added to the EC sensor chip and consequently precipitates TMB, resulting in an increase in current. In contrast, the biotinylated RP ssDNA is hydrolysed in the presence of viral target RNA (bottom row), cleaving the biotin group. Consequently, polystreptavidin-HRP does not bind to the surface of the chips, resulting in no TMB precipitation and no increase in current. b, Cyclic voltammogram showing the typical current peak signal achieved after incubation of samples from both SARS-CoV-2 negative (orange) and positive (blue) clinical samples. c, Clinical samples that contained SARS-CoV-2 viral RNA (+, blue circles, 19 samples) had low signals in our device and were clearly distinguishable from the high signals obtained for samples that did not contain viral RNA (−, orange circles and black line representing the median value, 11 samples). Student’s t-test ****P < 0.001.