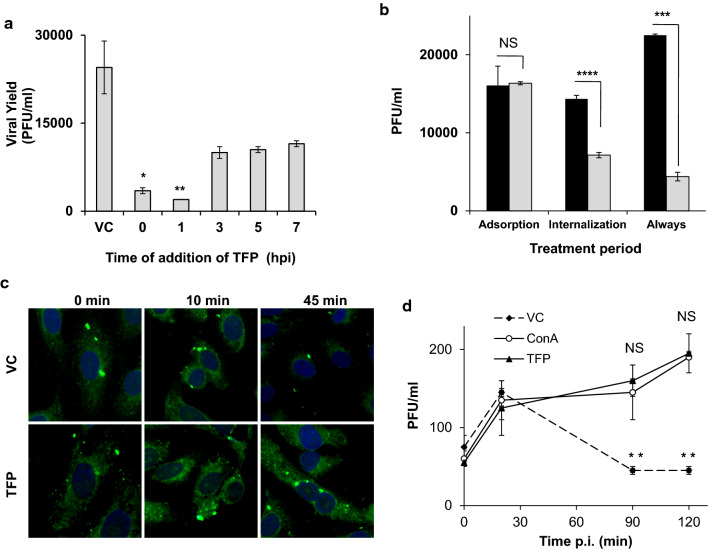
Fig. 4.
Mode of antiviral action of TFP: effect on virus entry. (a) Vero cells were infected with DENV-2, and 30 µM TFP was added simultaneously with virus (time 0) or at the indicated times after infection. Extracellular virus yields were determined at 24 h p.i. in all cell cultures. Statistical significance was evaluated using the nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis test. (b) DENV-2 was allowed to adsorb to Vero cells at 4°C for 1 h in MM with or without 30 µM TFP. Then, the amount of cell-bound infectious virus was determined by plaque assay (Adsorption). In other Vero cell cultures, DENV-2 was allowed to adsorb at 4°C for 1 h. After further incubation at 37°C for 1 h in MM with or without 30 µM TFP, cell monolayers were treated with proteinase K, and internalized virus was detected using an infectious center assay (Internalization). Finally, DENV-2 was allowed to adsorb at 4°C to another set of cultures, and after further incubation at 37°C for 24 h in MM with or without 30 µM TFP, virus yields in the cell supernatants were determined by plaque assay (Always). Statistical significance for each treatment was evaluated using Student's t-test. (c) DENV-2 was allowed to adsorb to Vero cells at 4°C in the absence (VC) or presence (TFP) of 30 µM TFP, and cultures were then shifted to 37°C. At 0, 10, and 45 min, cells were fixed and processed for immunofluorescence to detect the C protein. Cell nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258. (d) Vero cells were infected with DENV-2 for 1 h at 4°C and then incubated with MM (VC) or MM containing 30 µM TFP (TFP) or 50 nM concanamycin A (ConA). At different times post-adsorption, non-internalized virus was inactivated, cells were disrupted, and intracellular infectivity was determined. Statistical significance was evaluated using the nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis test. In a, b, and d, each value represents the mean of three independent experiments ± SD. NS, not significant; *, p < 0.05; **,p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; ****, p < 0.0001