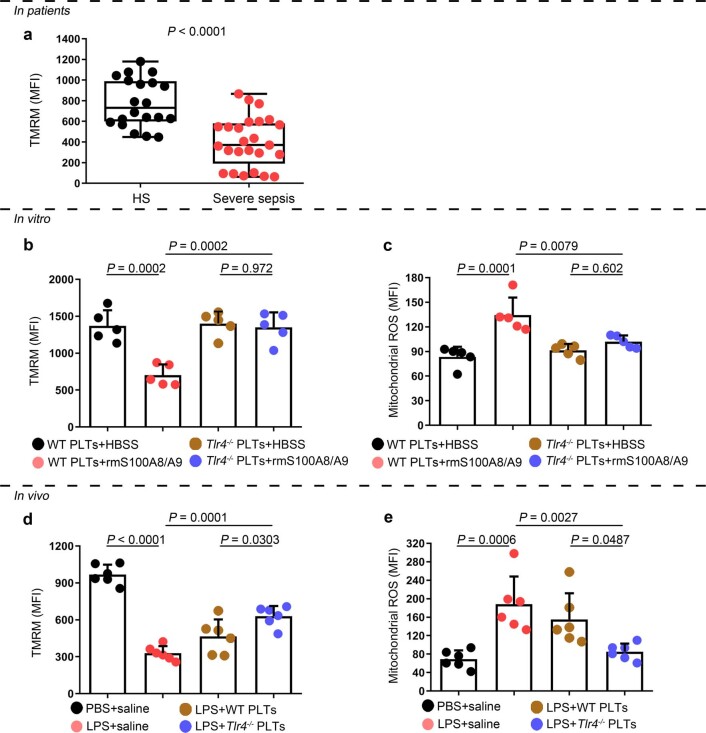
Extended Data Fig. 8. The function of mitochondria in septic platelets and S100A8/A9-induced platelets.
a, In platelets from severe sepsis (with or without septic shock) patients, bar graphs displaying change of mitochondrial membrane potential (∆Ψm) by staining with 40 nM TMRM using FACS analysis (HS: n = 20, Severe sepsis: n = 25). b, c, In vitro, bar graphs displaying change of mitochondrial ∆Ψm (b) and ROS production (c) in platelets (Tlr4-/- or WT) treated with 1 μg/ml rmS100A8/A9 for 4 hours using FACS analysis (n = 5). d, e, In the LPS induced murine model, mice with platelets depletion were transfused with a total of 1.2 ×107 purified platelets (volume: 200 μl, concentration: 6 ×1010 platelets/L) from Tlr4-/- or WT mice (n = 6/group). After 6 hours, bar graphs displaying change of mitochondrial ∆Ψm (d) and ROS production (e) in platelets (Tlr4-/–or WT) using FACS analysis (n = 6). Data was presented as mean fluorescence ± SD. Unpaired t test with two-tailed for a. One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test for b-e. Abbreviation is as follow: HS, healthy subjects; Severe sepsis, severe sepsis/septic shock; HBSS, hank’s balanced salt Solution. PBS, PBS-injected mice; LPS + saline, LPS-injected mice transfused with normal saline; LPS + WT PLTs, LPS-injected mice transfused with WT platelets; LPS + Tlr4-/- PLTs, LPS-injected mice transfused with Tlr4-/- platelets; TMRM, tetramethylrhodamine methyl ester; ROS, reactive oxygen species.