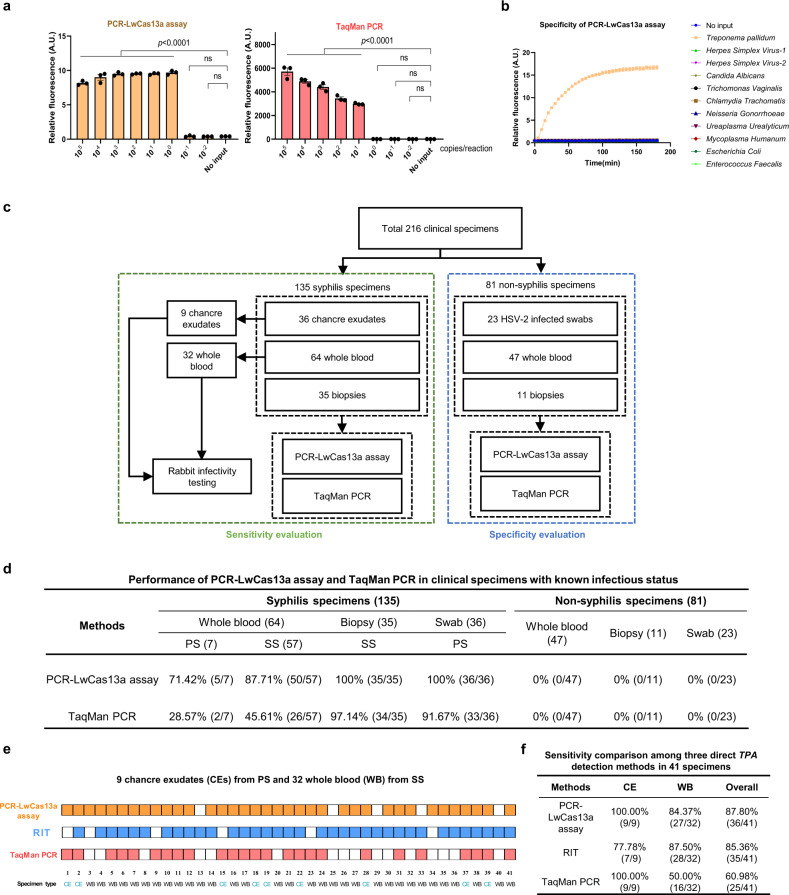
Fig. 2. Robust performance of the PCR-LwCas13a assay for detection of Treponema pallidum in clinical specimens.
a The PCR-LwCas13a assay exhibits excellent detection of the tpp47 gene and is an order of magnitude more sensitive than TaqMan PCR. b Evaluation of the specificity of the PCR-LwCas13a assay by testing DNA from a group of 10 genital microorganisms in 180 min of kinetics analysis. c Samples from 135 syphilis and 81 non-syphilis patients (216 total) were used to determine the clinical sensitivity and specificity of the PCR-LwCas13a assay in a parallel comparison with TaqMan PCR. Rabbit-infectivity testing (RIT) was performed on 9 chancre exudates and 32 whole blood samples from secondary syphilis. d Performance of the PCR-LwCas13a assay and TaqMan PCR with clinical specimens. e Comparison of direct detection with whole blood from 32 patients with secondary syphilis and chancre exudates from nine patients with primary syphilis. Squares with color (orange for PCR-LwCas13a assay, blue for rabbit-infectivity test, and red for TaqMan PCR) represent positive signals, while white squares represent negative results. Darkfield microscopy of testicular extracts was used to determine RIT results. f Comparison of the sensitivities of direct detection methods. Abbreviations: A.U. Arbitrary units, PS Primary syphilis, SS Secondary syphilis, CE Chancre exudate, WB Whole blood, RIT rabbit-infectivity test. n = 3 technical replicates; two-tailed Student t-test was used to analyze the statistical significance; p-value was labeled in the figure, ns = not significant; error bars represent mean ± SEM. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.