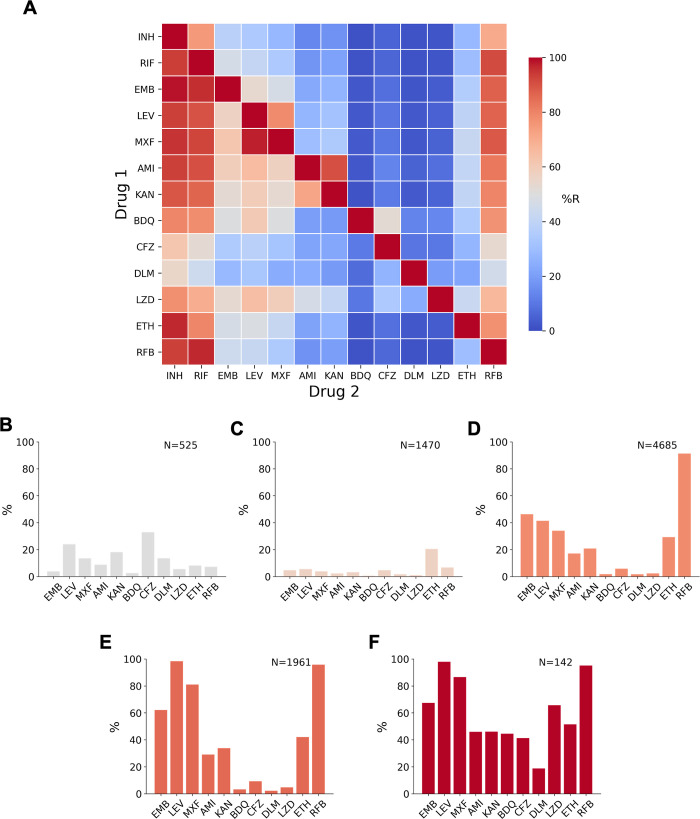
Fig 4. Co-occurrence of resistance to 1 drug conditional on resistance to another drug, or to resistance background.
(A) The heatmap shows the probability of an isolate being resistant to Drug 2 if it is resistant to Drug 1, percentages are given in Table F in S1 File. (B-F) Percentage of isolates that are resistant to another of the 13 drugs in a background of (B) isoniazid susceptible + rifampicin susceptible (but resistant to at least one other antitubercular drug), (C) isoniazid resistant + rifampicin susceptible, (D) MDR/RR, (E) Pre-XDR, and (F) XDR. Only samples with definite phenotypes for RIF in MDR backgrounds and RIF and INH in non-MDR backgrounds and the additional drug are included. AMI, amikacin; BDQ, bedaquiline; CFZ, clofazimine; CRyPTIC, Comprehensive Resistance Prediction for Tuberculosis: an International Consortium; DLM, delamanid; EMB, ethambutol; ETH, ethionamide; INH, isoniazid; KAN, kanamycin; LEV, levofloxacin; LZD, linezolid; MDR, multidrug resistant (resistant to first-line drugs isoniazid and rifampicin); MXF, moxifloxacin; pre-XDR, pre-extensively drug resistant (MDR/RR + fluoroquinolone resistant); RFB, rifabutin; RIF, rifampicin; RR, rifampicin resistant; XDR, extensively drug resistant (MDR/RR + resistant to at least 1 fluoroquinolone and either bedaquiline or linezolid).