Figure 6.
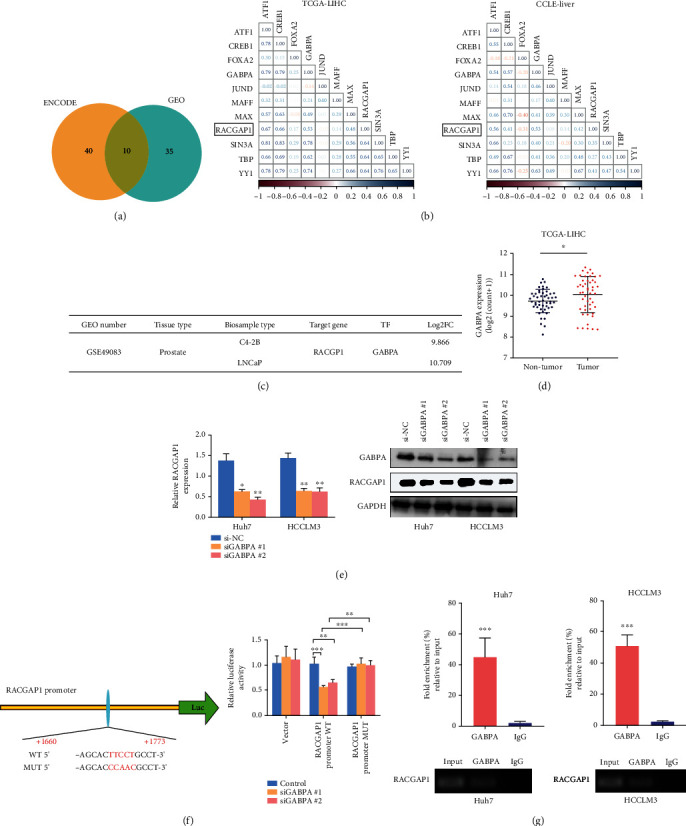
Excessive activation of GABPA promoted RACGAP1 transcription in HCC. (a) Total ten transcription factors (TFs) were intersected from ENCODE and GEO database by Veen. (b) The correlations of ten TFs with RACGAP1 in TCGA-LIHC and CCLE-Liver. (c) RACGAP1 was obviously changed with knockdown of GABPA in prostate tissues in GSE49083. (d) GABPA had higher expression in HCC compared with non-tumor tissues. (e) The efficiency of GABPA knockdown in Huh7 and HCCLM3 cell lines. (f) Schematic diagram of GABPA binding site on RACGAP1 promoter and the mutant RACGAP1 promoter (left panel); Inactivation of GABPA obviously reduced wild type but not mutant RACGAP1 promoter luciferase activity (right panel). (g) Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay showed GABPA binding to the promoter of RACGAP1 in Huh7 and HCCLM3 cells.∗p <0.05; ∗∗p <0.01; ∗∗∗p <0.001.
