Figure 2.
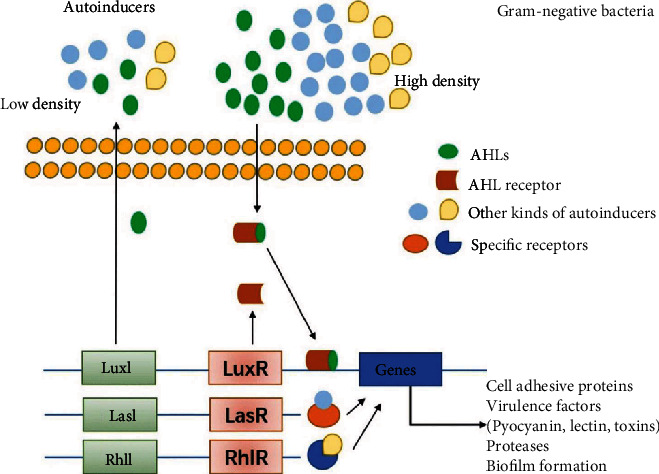
QS mechanism in gram-categorized species. In gram− bacteria biofilm formation, QS signaling involve autoinducer acyl-homoserine lactones (AHLs) that help communication among bacteria and modulate targeted genes expression by activating corresponding cytoplasmic receptors. The Luxl/luxR transcriptional factors are other essential regulating factors activated by AHLs and control the expression of various virulence factors in different gram− bacteria such as pigments, carbohydrate-binding proteins, various proteases such as elastase, toxin, different autoinducers such as Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS), CAI-1, and AI-2, as well as QS receptors such as LasI/LasR, RhlI/RhlR, CqsS, and LuxPQ. Specific autoinducers can also further promote other adhesives and virulence factors [69].
