Figure 5.
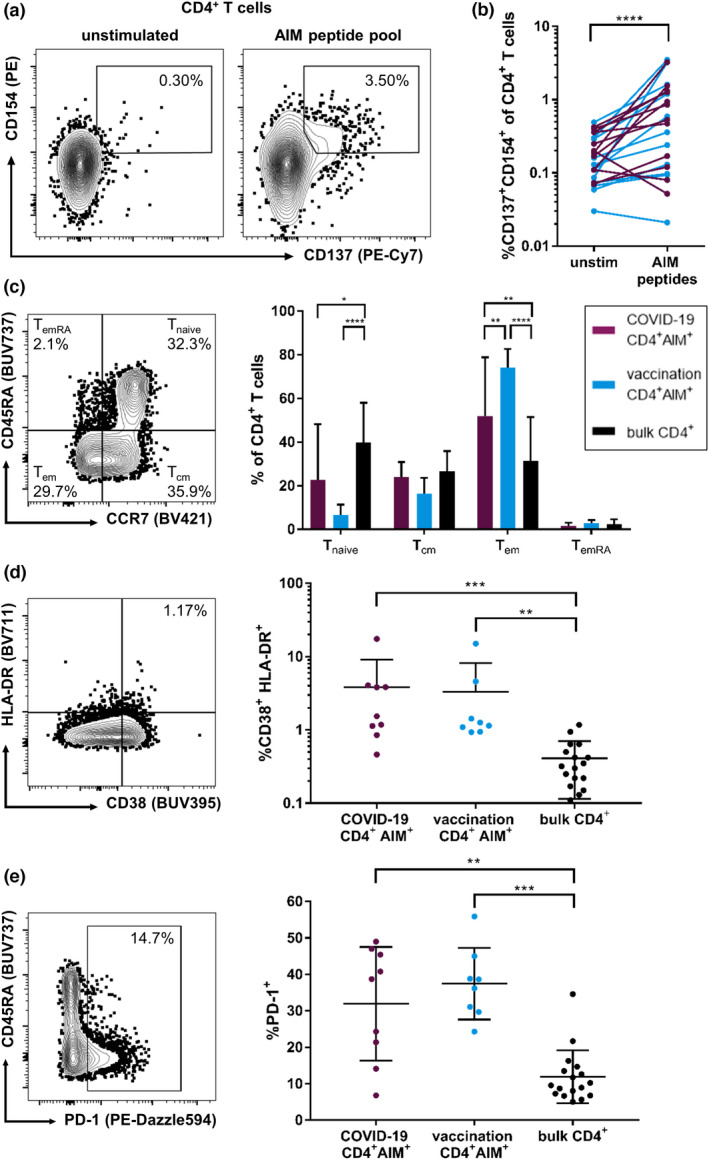
Frequencies and phenotype of AIM+ CD4+ T cells in response to a spike glycoprotein peptide pool. Thawed PBMCs were stimulated for 18 h with the peptide pool or SEB (positive control) or were left untreated (negative control) and analysed by flow cytometry. Antigen‐reactive CD4+ T cells were defined as CD137+CD154+ (a). After stimulation with the peptides, an increase in AIM+ (CD137+CD154+) CD4+ T cells could be observed in most individuals except for a few non‐responders (SI ≤ 1.5) (b). Non‐responders were excluded from further analyses. Memory phenotype of AIM+ CD4+ T cells of individuals with COVID‐19 or vaccination in comparison with bulk CD4+ T cells (c). AIM+ CD4+ T cells of individuals with COVID‐19 and vaccinated individuals show significantly higher proportions of activation markers CD38 and HLA‐DR than bulk CD4+ T cells (d). PD‐1 expression is increased in AIM+ CD4+ T cells of individuals with COVID‐19 and vaccination compared with that in bulk CD4+ T cells (e). Data are expressed as mean with standard deviation. * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001; and **** P < 0.0001.
