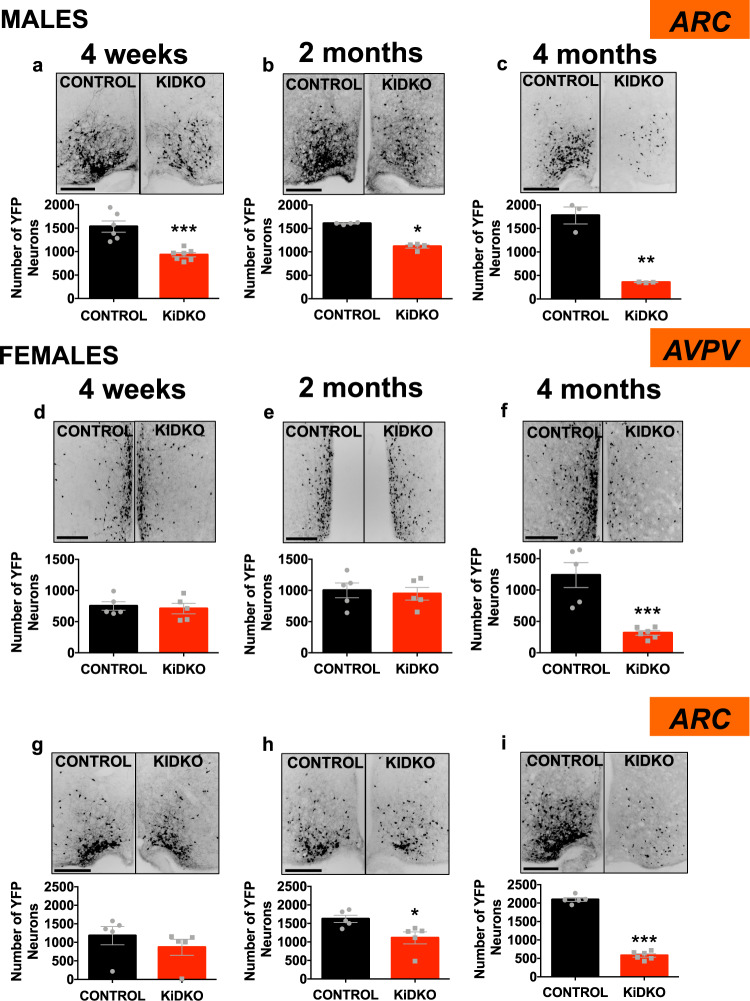
Fig. 6. Kiss1 neuronal survival in the hypothalamus of KiDKO mice along postnatal maturation.
Labeling of viable Kiss1 neurons in vivo was achieved by using a triple transgenic mouse line, expressing the Cre-dependent reporter (ROSA26)-YFP in Kiss1 neurons upon a KiDKO background. In this mouse line, cells ever expressing Kiss1 become persistently labeled with the fluorescent marker YFP, even if they stop expressing Kiss1. Representative images and quantitative data on YFP-positive cells in the ARC of males (a–c) and the AVPV (d–f) and ARC (g–i) of females of control and KiDKO genotypes are presented. Data were collected at three postnatal ages: 4 weeks (corresponding to early pubertal transition); and two periods of adulthood (2- and 4-months). Group sizes: n = 6, 4, and 3 for 4 weeks, 2 months, and 4 months, control males, respectively; n = 7, 4, and 3 for 4 weeks, 2 months, and 4 months KiDKO males, respectively; n = 5 for all control females; n = 5, 5, and 6 for 4 weeks, 2 months, and 4 months KiDKO females, respectively. The values are represented as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 vs. corresponding control groups. Scale bars correspond to 200 µm.