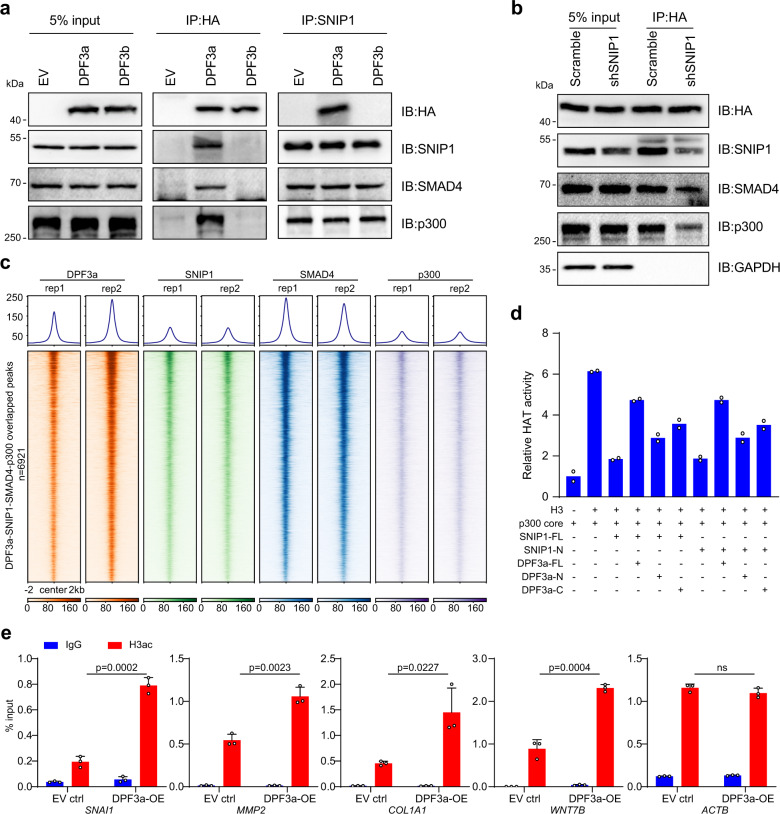
Fig. 6. DPF3a-SNIP1 binding released the inhibitory effect of SNIP1 on p300 activity.
a DPF3a, SNIP1, SMAD4, and p300 form in a complex. HA-tagged DPF3a or endogenous SNIP1 protein was immunoprecipitated and followed by immunoblotting using antibodies against SMAD4 and p300 to detect the co-precipitated endogenous SMAD4 and p300. Three independent experiments were performed and similar results were obtained. b SNIP1 bridges DPF3a to SMAD4 and p300. SNIP1 was knocked down in 786-O cells using shRNA. HA-tagged DPF3a protein was immunoprecipitated using anti-HA magnetic beads and followed by immunoblotting using antibodies against SNIP1, SMAD4, and p300 to detect the co-precipitated endogenous SNIP1, SMAD4, and p300. Input lanes represent 5% of total protein lysate. Three independent experiments were performed and similar results were obtained. c Co-occupancy of DPF3a, SNIP1, SMAD4, and p300 on the genome. Average profiles and heatmaps of normalized read density of ChIP-seq for DPF3a, SNIP1, p300, and SMAD4 overlapped peaks (n = 6,921). DPF3a and SNIP1 ChIP-seq data used in this figure are identical to the data used in Fig. 5f. d DPF3a releases SNIP1-mediated inhibition of p300 HAT activity in vitro. In vitro HAT activity assays of p300 in the presence of recombinant full-length SNIP1 (FL) or its N-terminus in combination with full-length DPF3a (FL), its N-terminus or C-terminus. Data were presented as mean values (n = 2 independent experiments). e Overexpression of DPF3a enhances local histone acetylation at specific loci. Pan-H3ac ChIP experiments were performed and H3ac enrichment at selected regions in DPF3a-OE cells was compared to EV control. Enrichment of H3ac was quantified by qPCR. Data were presented as mean values ± SD (n = 3 independent experiments). Statistical significance was estimated using a two-sided student t-test. Source data are provided in the Source Data file.