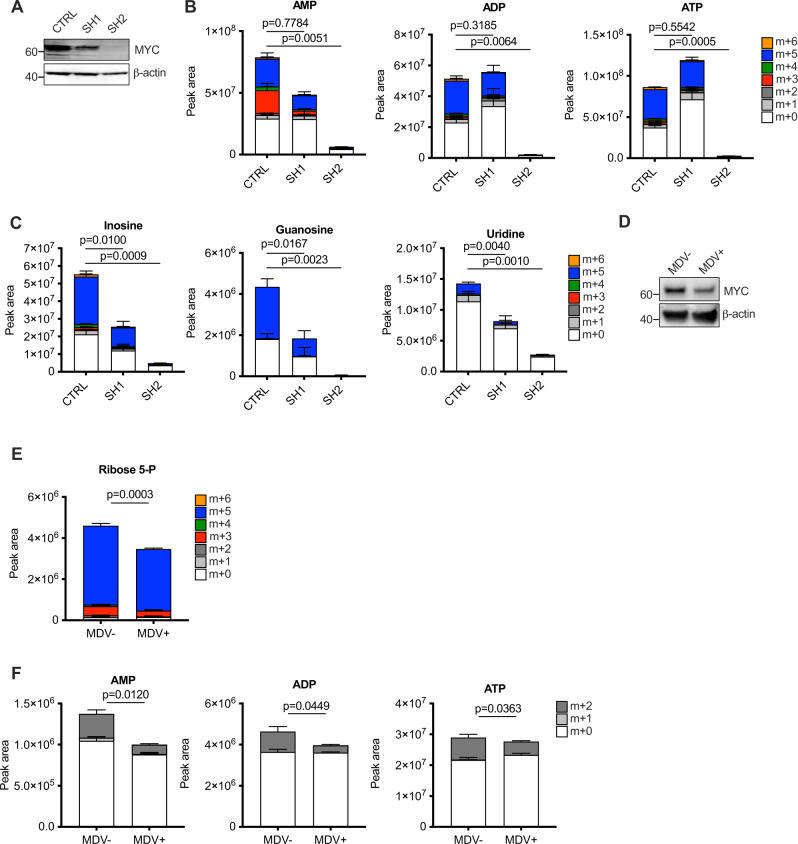
Fig. 4. Induction of nucleotide biosynthesis, catabolism and PPP remodelling is dependent upon MYC in MYC-driven cancer cells.
LC-MS was used to quantify isotopologues of metabolites following 13C6-glucose pulse in RAJI Burkitt’s lymphoma (A–C) and Myc-caP mouse prostate cancer cells (D–F). A Western blot showing shRNA-mediated knockdown of MYC in Raji cells. B, C Incorporation of 13C6-glucose with a 6 h pulse into (B) adenine nucleotides and (C) nucleosides. An ordinary one-way ANOVA was used to determine statistical significance for the m + 5 isotopologue (n = 3 biological replicates). D Western blot showing reduction of MYC levels upon 96 h enzalutamide (MDV) treatment in Myc-caP cells. E, F Incorporation of (E) Incorporation of 13C6-glucose into ribose 5-phosphate with a 5 min pulse and (F) 15N-glutamine into adenine nucleotides with a 6 h pulse in Myc-caP cells treated for 48 h with enzalutamide (MDV). An ordinary one-way ANOVA was used to determine statistical significance for the m + 5 or m + 2 isotopologue for (E) and (F), respectively (n = 3 biological replicates). For all statistical tests, P ≤ 0.05 was considered significant and error bars show the standard error of the mean.