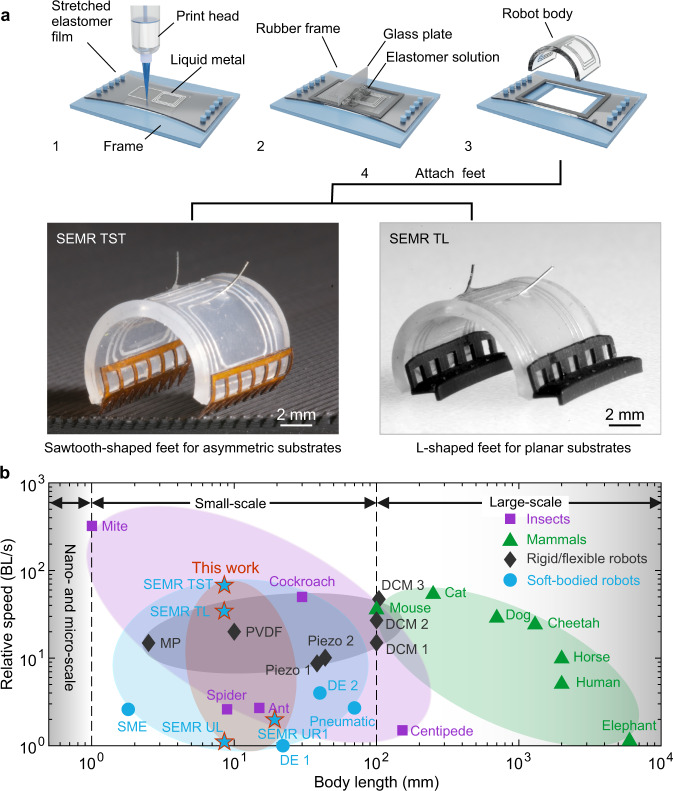
Fig. 1. Fabrication and performance of SEMRs.
a Schematic of the fabrication process. LM coils are printed on a prestretched elastomeric film. Then, the elastomer precursor solution is applied on top of the LM coils using bar coating, resulting in a bilayer structure from which the robot body is cut out. Lastly, sawtooth-shaped or L-shaped feet are attached. For actuation, the robots are connected to the external power with electrodes. b Maximum running speeds of representative mammals, arthropods, soft robots, and robots versus body length. Shaded areas encompass the ranges for different categories, as indicated by the symbols in the legend, and for our SEMRs, which are labeled with the stars. The maximum relative speed of our SEMRs is 70 BL/s, almost 17.5 times larger than for the previous soft-bodied robots, faster than centimeter-scale electromagnetic robots and most fast animals. Two stars with the higher speed correspond to tethered SEMRs, and two slower ones to untethered robots. Details can be found in Supplementary Table 1.