Figure 4.
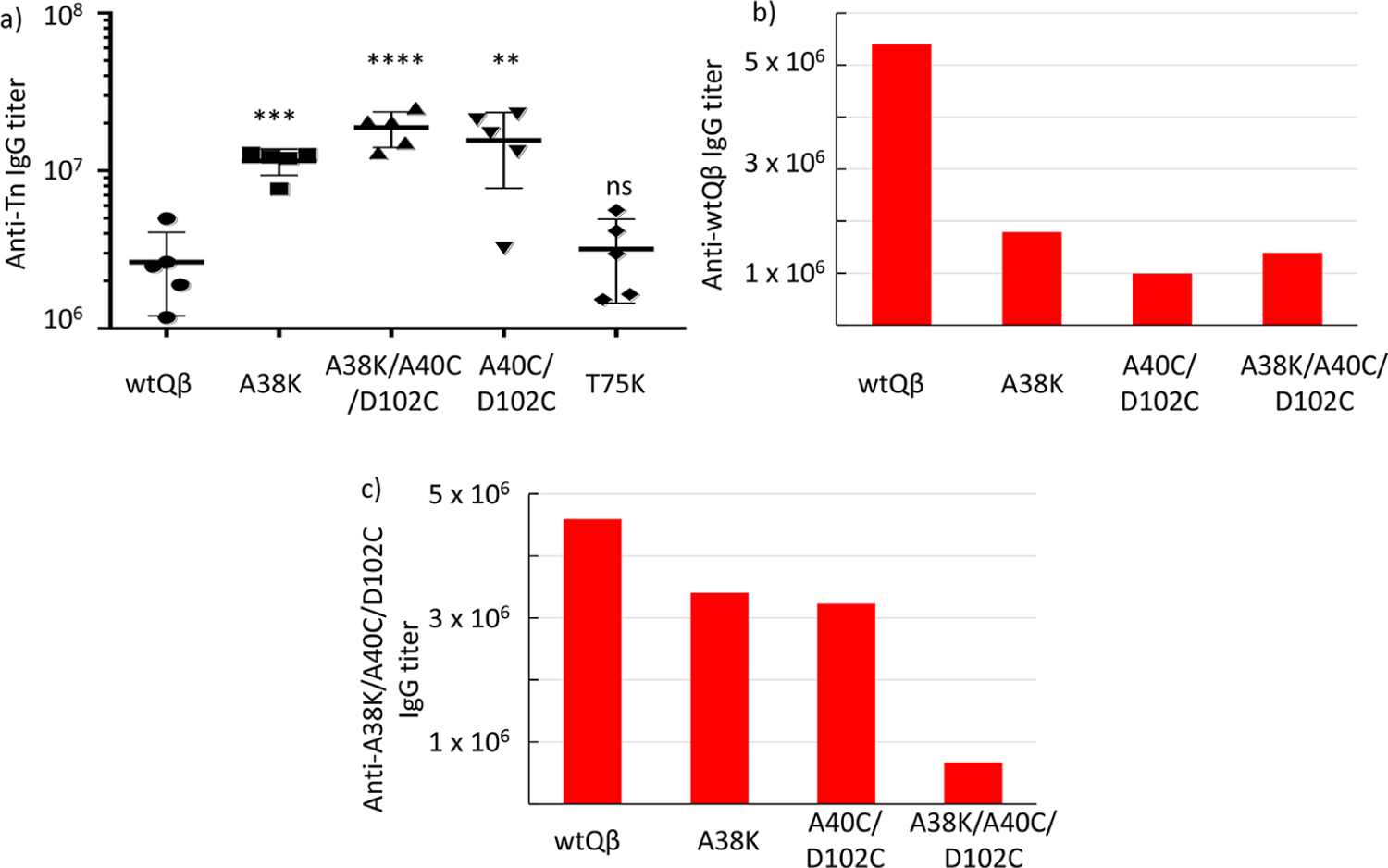
(a) Anti-Tn IgG titers of postimmunized sera (day 35) from groups of mice (n = 5) vaccinated with various mQβ-Tn conjugates assayed against BSA-Tn as the coating antigen for ELISA. The statistical significance between a mQβ and wtQβ was determined by the Student t test using GraphPad Prism (**p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; ns, not significant). Titers of (b) anti-wtQβ and (c) anti-mQβ(A38K/A40C/D102C) IgG antibodies in postimmunized sera (day 35) from groups of mice (n = 5) vaccinated with wtQβ, mQβ(A38K), mQβ(A40C/D102C), and mQβ(A38K/A40C/D102C) conjugates, respectively. The mQβ(A38K/A40C/D102C)-Tn conjugate induced higher titers of anti-Tn IgG antibodies with reduced antibody responses against both wtQβ and mQβ(A38K/A40C/D102C).
