Figure 2. Pooled Estimates for Bleeding Events and Cardiovascular Events.
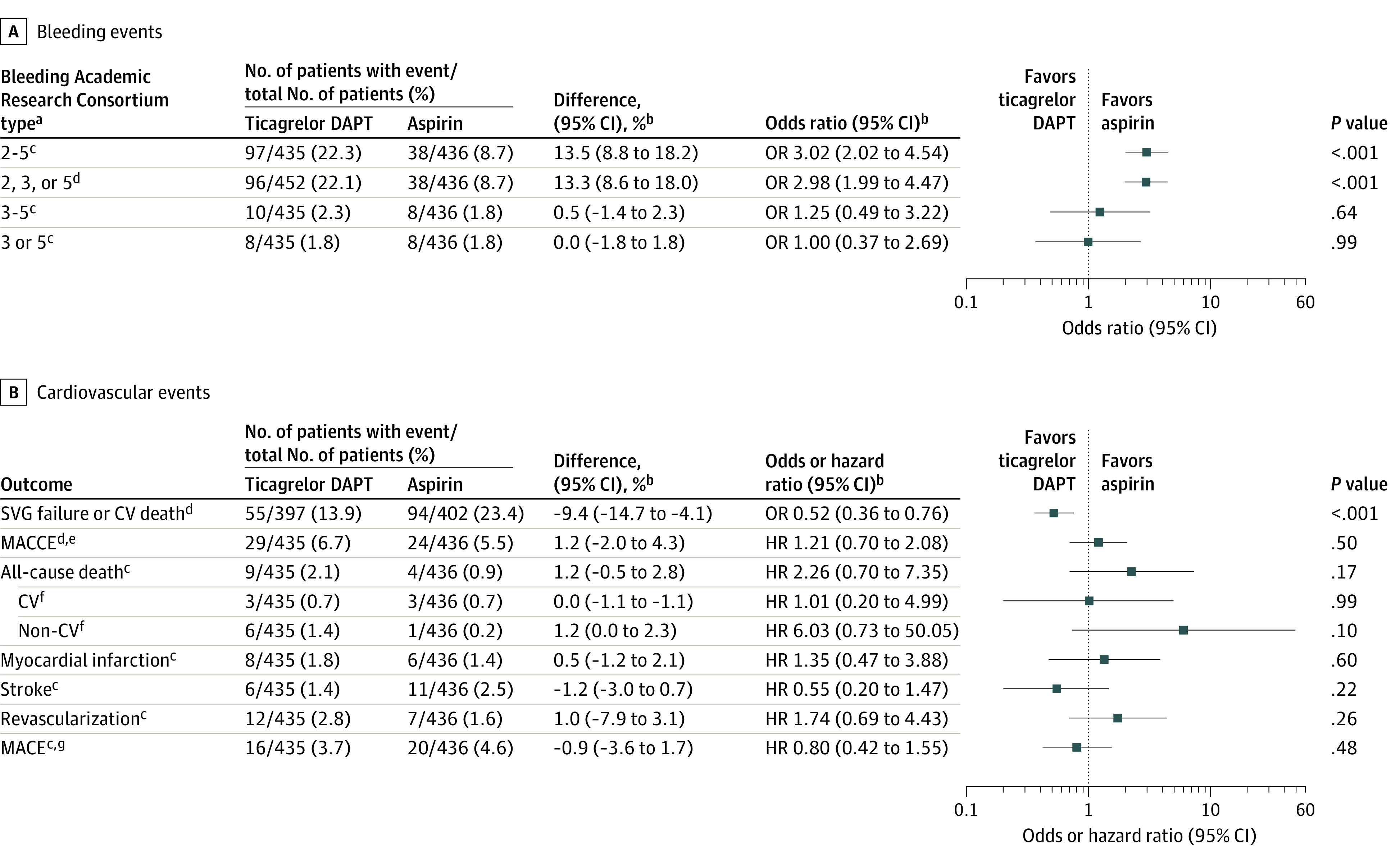
aType 0 indicates no bleeding; type 1, bleeding that is not actionable and does not cause the patient to seek unscheduled performance of studies, hospitalization, or treatment; type 2, any overt, actionable sign of hemorrhage (eg, bleeding that does not fit type 3, 4, or 5 criteria but meets at least 1 of the following: [1] requires nonsurgical medical intervention, [2] leads to hospitalization or increased level of care, or [3] prompts evaluation); type 3a, overt bleeding plus hemoglobin drop of 3 to 5 g/dL (provided hemoglobin drop is related to the bleeding event) or any transfusion with overt bleeding; 3b, overt bleeding plus hemoglobin drop of 5 g/dL (provided hemoglobin drop is related to the bleeding event), cardiac tamponade, bleeding requiring surgical intervention for control (excluding dental, nasal, skin, or hemorrhoid), and bleeding requiring intravenous vasoactive agents; 3c, intracranial hemorrhage (does not include microbleeds or hemorrhagic transformation, does include intraspinal), subcategories confirmed by autopsy or imaging or lumbar puncture, intraocular bleed compromising vision; type 4, coronary artery bypass graft surgery–related bleeding; and type 5, fatal bleeding.
bAdjusted by trial.
cPost hoc outcomes.
dSecondary outcome.
eDefined as the composite of all-cause death, myocardial infarction, stroke, or revascularization.
fAdditional outcomes.
gDefined as the composite of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, or stroke.
Includes patients from the TAP-CABG,8 DACAB,9 and POPular CABG10 trials. See the Methods section for the full names of the studies.
CV indicates cardiovascular; DAPT, dual antiplatelet therapy; HR, hazard ratio; MACCE, major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular event; MACE, major adverse cardiovascular event; OR, odds ratio; SVG, saphenous vein graft.
