Figure 6.
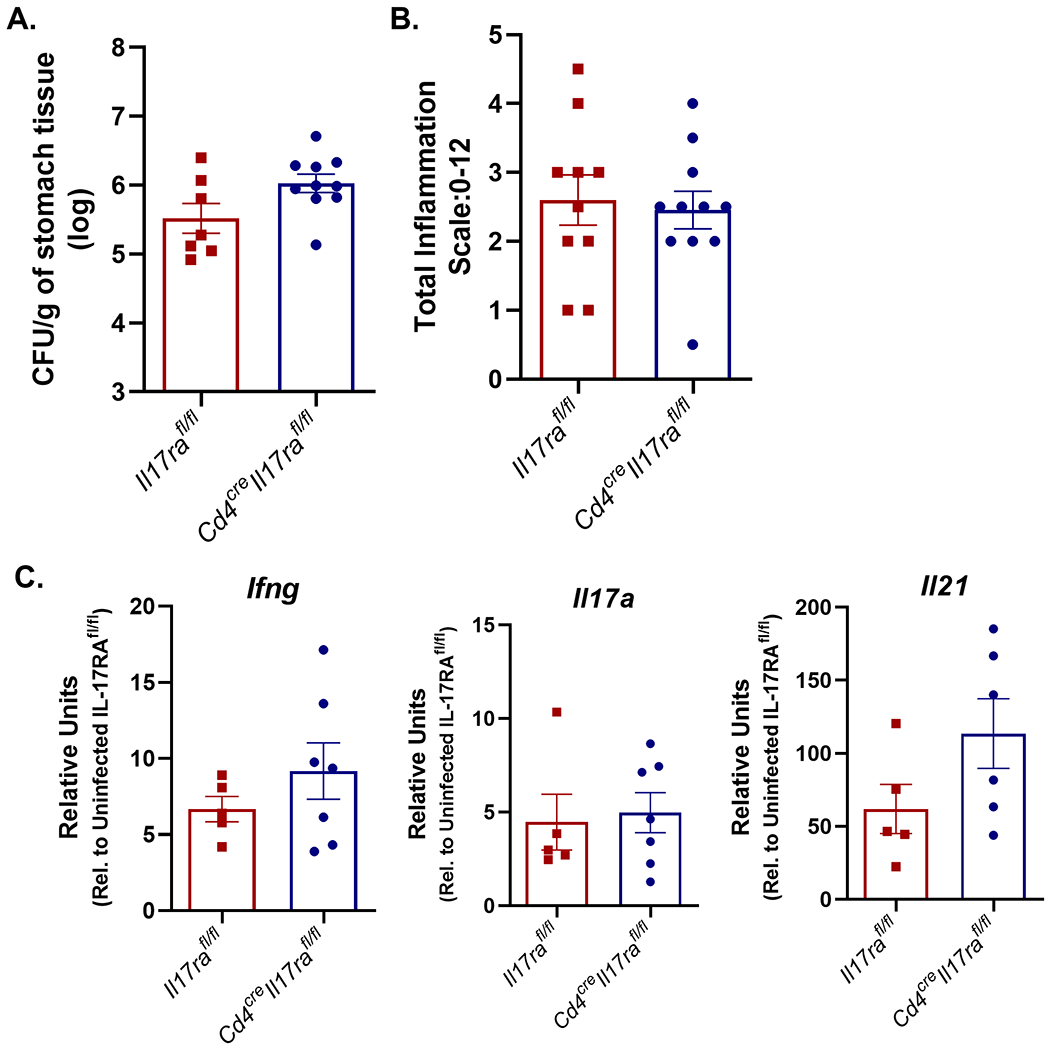
IL-17RA expression on T cells is required to control bacterial burden but not required to control gastric inflammation in the mouse model. A) Bacterial burden was measured in Il17rafl/fl (WT) and Cd4creIl17rafl/fl mice that were infected with PMSS1 for 3 months (8-11 per genotype). Colony forming units (CFU) per gram of stomach tissues was calculated and is presented in the graph ±SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using Mann Whitney U unpaired t test on log transformed CFU/gram data. These data are representative of 2 independent experiments. B) Levels of acute and chronic inflammation were scored on stomach tissue (in the corpus and antrum) at 3 months post infection with strain PMSS1. Total inflammation as presented is the sum of acute and chronic inflammation (8-10 per genotype). Statistical analysis was performed using Kruskal-Wallis test’s and the Dunn’s multiple comparisons test which resulted in no significant difference between genotypes. See methods for scoring system (scale is 0–12). Error bars represented mean ± SEM and are representative of 2 independent experiments. C) qPCR was used to measure Il21, Il17a and Ifng transcripts in the gastric tissue of H. pylori–infected Il17rafl/fl and infected Cd4creIl17rafl/fl mice (5-7 per genotype). Relative units are calculated as described in the methods, relative to Gapdh and calibrated to uninfected WT mice. pPCR data is representative of 2 independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed using an ANOVA analysis and Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Error bars represent ± SEM; *P ≤ 0.05, **, P ≤ 0.01 compared to the uninfected group.
