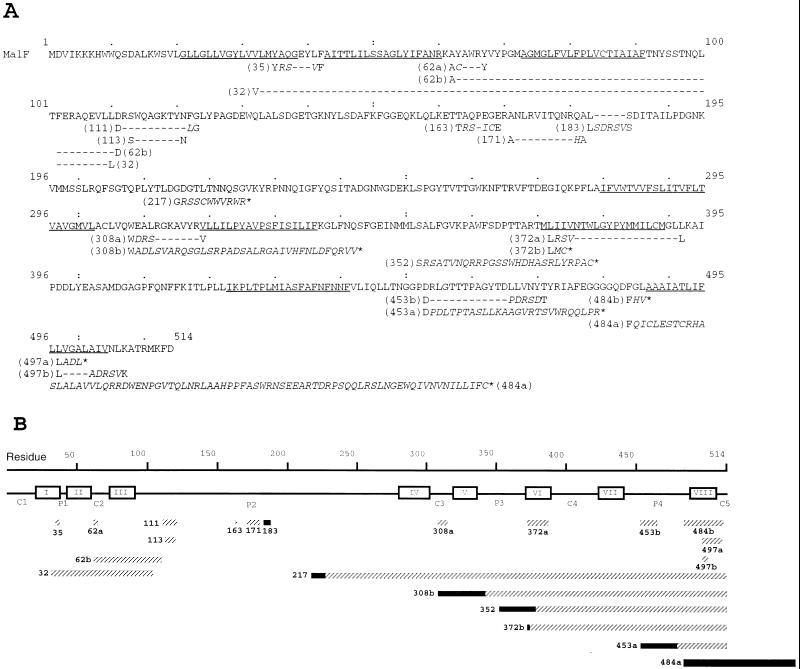
FIG. 2.
Mutations in protein MalF. The derivatives of malF were sequenced with the Sequenase version 2.0 DNA sequencing kit (U.S. Biochemical and Amersham) with [α-33P]dATP (ICN). Oligonucleotides (Eurogentec) corresponding to 12 segments of the malF gene were used as primers. The approximate location of the insertion was first determined by restriction enzyme analysis, and then the appropriate primer was chosen. In some cases, the sequencing of the antiparallel strand was carried out to resolve ambiguities. (A) Sequences of wild-type MalF and the collection of mutants described in this work. Predicted α-helices are shown underlined in the wild-type sequence. In mutant sequences, amino acids inserted are shown in italics between the positions of original MalF amino acids. Each mutant is named according to the last nonmodified amino acid. Hyphens denote deletions. Stop codons in the frameshift mutations are indicated by asterisks. (B) Mutations in MalF protein, represented schematically in a linear fashion. Predicted TM segments are boxed and numbered in roman numbers. The lengths of rectangles are proportional to the sizes of deletions (solid) or insertions (hatched).