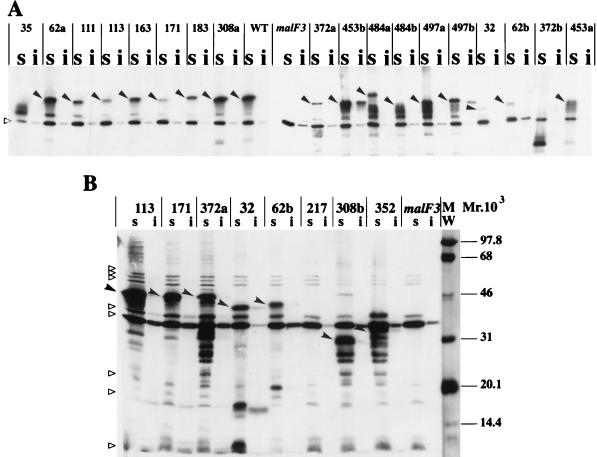
FIG. 3.
Subcellular localization of MalF mutant proteins. Cells were induced at an A600 of 0.5 with 1 mM IPTG. Cell fractionation was performed according to the method described in reference 20, with the following modifications. The protease inhibitor PEFABLOC (Interchim) was added at an 0.5 mM final concentration to all buffers. Membrane extracts were recovered after 1 h of centrifugation at 20,000 × g. To solubilize cytoplasmic membrane proteins, Triton X-100 was used as described in reference 15. Equivalent volumes of Triton-soluble (s) and Triton-insoluble (i) fractions were mixed with an equal volume of double-strength sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis loading buffer, boiled for 5 min in a water bath, loaded onto sodium dodecyl sulfate–12% (wt/vol) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gels, and subjected to immunoblotting. Nitrocellulose membranes were probed with the specific antibody and with a horseradish peroxidase anti-rabbit immunoglobulin conjugate (Bio-Rad). Immune complexes were revealed by ECL Western blotting detection reagents (Amersham). Relative intensities were quantified by scanning the ECL films with an Image Master VDS apparatus (Pharmacia Biotech). The solid arrowheads indicate the full-length MalF mutant proteins. The empty triangles indicate cross-reacting proteins that are visible in all lanes. The amount of protein loaded in immunoblot B was threefold higher than that loaded in immunoblot A. WT, wild type. MW, molecular weight markers, in thousands.