Figure 6.
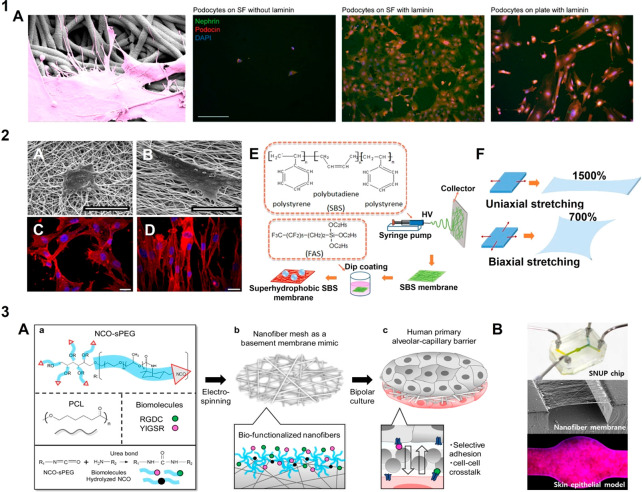
Fibrous basement membrane mimics: Electrospinning is a versatile technique to produce fibrous scaffolds of varying properties in order to mimic the native BM in terms of architecture strength and dimensions of the fibers: (1A) A laminin-coated nanofibrous membrane of silk fibroin (SF) was fabricated as glomerular BM mimic, for differentiation of human podocytes from human stem cells, where (A) a podocyte interacts with the laminin coated SF fibers and confocal images of podocytes stained for podocin (red), nephrin (green) and nucleus (blue), on SF without laminin, SF with laminin and on tissue culture plate; adapted with permission from ref (277). Copyright 2022 Mou, Xingrui et al. https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ (changes were made). (2) Varying mechanical and topographical properties is possible where (A–D) random and aligned forms of PCL-gelatin meshes are exploited to mimic specific BM, where NIH3T3 cells are shown to respond respectively by cellular spread or elongation; adapted with permission from ref (295). Copyright 2016 Fee et al. https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ (changes were made). (E,F) optimization of elastic modulus can be achieved where superhydrophobic and elastic fibers were fabricated by dip coating poly(styrene–butadiene-styrene) (PBS) fibers in fluoroalkyl silane (FAS) to produce fibers that can be stretched both uniaxially (1500%) and biaxially (700%) even after 1000 stretch cycles; adapted with permission from ref (296). Copyright 2015 Hua Zhou et al. http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ (changes were made). (3) Electrospinning allows biofunctionalization as seen in (A) synthetic alveolar-capillary BM for in vitro expansion and study of pulmonary cells, where electrospinning of PCL and the surface segregated isocynate end groups of six-armed sPEG form covalent bonds with the amine groups of bioactive peptides via urea bond formation; reprinted with permission from ref (41). Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society (no changes); (B) Electrospun fibers can also be used as free-standing membranes in microfluidic chips to analyze effect of dynamic shear on cells; reprinted with permission from ref (297). Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society (changes were made).