FIGURE 1.
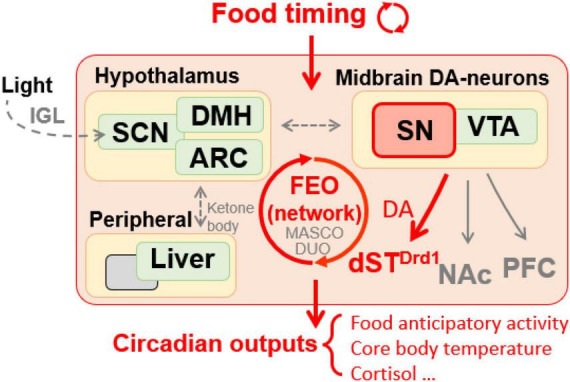
Food timing, particularly when restricted temporally, is a potent zeitgeber entraining an oscillatory system in the brain, relaying rhythmic behavior outputs. DA signaling is required in SN neurons projecting to the dorsal striatum but not the NAc or PFC to mediate food anticipatory activity. Peripheral oscillators, like the liver, may contribute to food entrainment via ketone bodies secretion to unknown brain target(s). Hypothalamic areas are also suggested to be involved in food entrainment regulation. Ambient light pathway via IGL influences the proper development of SCN structure which is necessary for proper food entrainment. SN, substantia nigra; VTA, ventral tegmental area; ARC, arcuate nucleus; DMH, dorsomedial hypothalamus; SCN, suprachiasmatic nucleus; IGL, intergeniculate leaflet; Drd1, D1 dopamine receptor; dST, dorsal striatum; NAc, nucleus accumbens; PFC, prefrontal cortex; FEO, food entrainable oscillator; MASCO, methamphetamine-sensitive circadian oscillator; DUO, dopaminergic ultradian oscillator.
