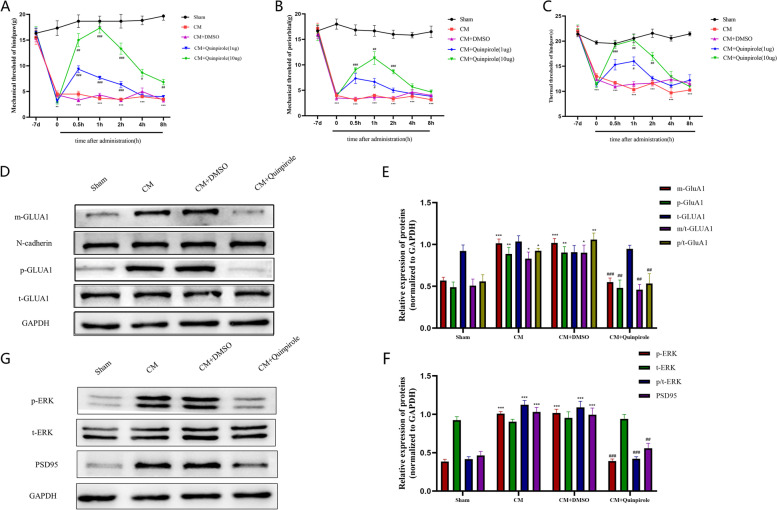
Fig. 3.
Effect of quinpirole on pain thresholds and GLUA1 trafficking in CM rats. A B and C Pain thresholds were increased after quinpirole (1 µg and 10 µg) administration in CM rats in a dose-dependent manner. Two-way ANOVA with the Bonferroni post hoc test. n = 6/group. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. the Sham group; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. the CM + DMSO group. D and E Western blot showing enhanced GLUA1 trafficking and increased phosphorylation levels in the CM group, which were abolished by DRD2 agonist treatment; the total GLUA1 level was unchanged. p-GLUA1, m-GLUA1 and t-GLUA1 represent the phosphorylated, plasma membrane and total levels of GLUA1 respectively. p/t-GLUA1 represents the p-GLUA1/t-GLUA1 value; m/t-GLUA1 represents the (m-GLUA1/N-cadherin)/(t-GLUA1/GAPDH) value. F and G The increases in the protein levels of PSD95 and phosphorylated ERK in CM rats were dramatically inhibited by quinpirole, as shown by western blot analysis. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test; n = 6/group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. the Sham group; ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 vs. the CM + DMSO group