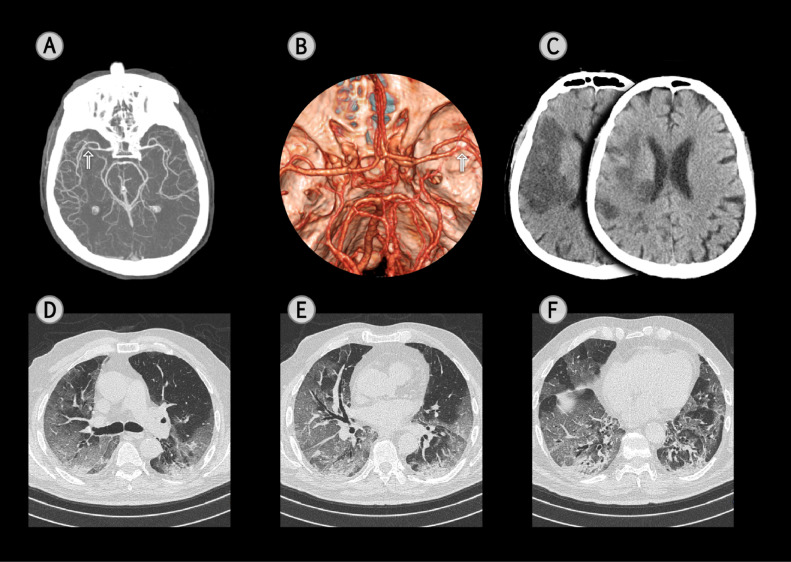
Fig. 1.
A Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) of a 65-year-old male, COVID-19-associated stroke patient, with left hemiparesis and neglect (NIHSS 18) after having had a temperature, cough and dyspnea for 7 days. The arterial phase of the CTA evidences a steno-occlusion of right middle cerebral artery (arrow) (A: maximum intensity projection; B: volume rendering technique with top view). A head Computed Tomography scan (CT), performed 24 hrs. later, documented an extensive ischaemic lesion in the right temporal and frontal lobes (C). A chest CT scan, on the 2nd day after admission, for respiratory symptoms, evidenced a bilateral reticular pattern, superimposed on a background of ground-glass opacities (GGO) (D-F) and bibasilar subpleural consolidations (F). Fibrous stripes and multiple small vascular enlargement were also observed (E and F). Well aerated lung with a visual score of 40%.