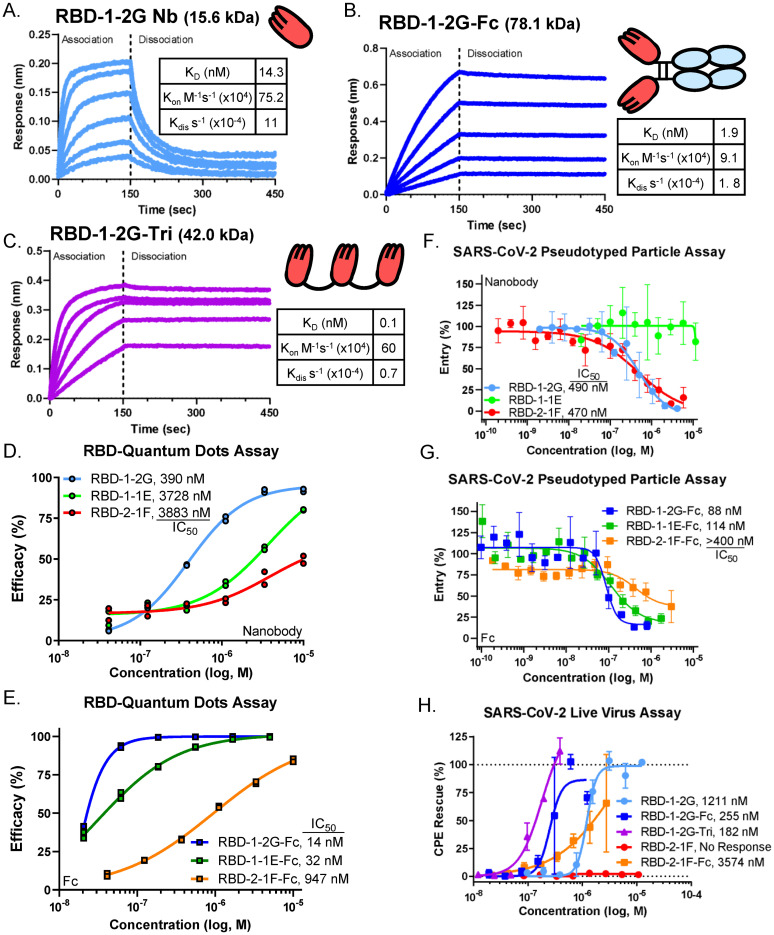
Fig 2. Multivalency improves affinity and inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro.
(A-C) Bio-layer interferometry binding profiles for the (A) RBD-1-2G Nb, (B) RBD-1-2G-Fc and (C) RBD-1-2G-Trimer against RBD-His (100 nM to 6.25 nM, 1:2 dilution). (D-E) QD endocytosis assay using QD608-RBD and ACE2-GFP HEK293T cells to visualize receptor binding. Nanobody efficacy in reducing RBD internalization by (D) Nanobody and (E) Fc constructs. N = duplicate wells, approximately 2500 cells and 1600 cells, respectively. (F-G) SARS-CoV-2 pseudotyped particle entry assay using HEK293-ACE2 cells as target. Inhibition of pseudotyped particle entry was tested for Nanobody(F) and Fc(G) constructs Representative data from two independent experiments. Data represents mean inhibition per concentration (n = 3), all error bars represent SEM. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 live virus infection with the RBD-1-2G and RBD-2-1F in various formats. Representative biological replicate with n = 2. Technical replicates are n = 2 per concentration, all error bars represent S.D.