FIGURE 3.
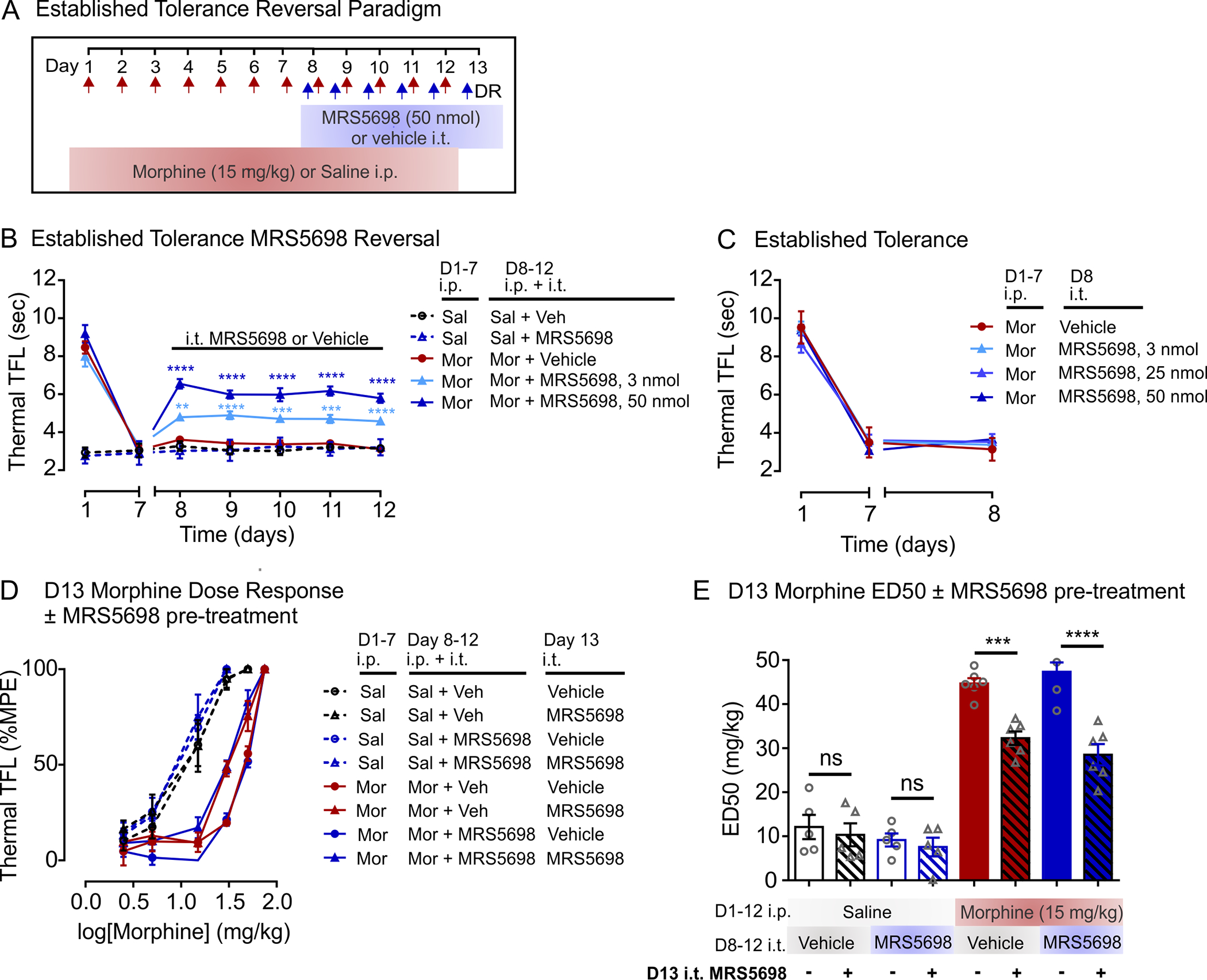
Spinal A3AR activation partially restores morphine antinociception in morphine-tolerant rats. (a) Schematic of drug administration paradigm. (b,c) Effect of intrathecal injection of MRS5698 in rats with established morphine tolerance. (b) Co-treatment of intrathecal MRS5698 or vehicle injection with morphine (15 mg/kg; i.p) or saline (i.p) on days 8–12. Sal + Veh n = 6, Sal + MRS5698 n = 6, Mor + Veh n = 8, Mor + MRS5698 3 nmol n = 7, Mor + MRS5698 50 nmol n = 7. Two-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s post hoc test (Interaction F(24,174) = 23.34, p < 0.0001; Time F(6,174) = 97.94, p < 0.0001; Treatment F(4,29) = 90.15, p < 0.0001). *Significance compared to Sal + MRS5698 (Mor + MRS5698 50 nmol (D8–12 p < 0.0001) and Mor + MRS5698 3 nmol (D8 p = 0.0014, D9 p < 0.0001, D10 p = 0.0002, D11 p = 0.0005, D12 p < 0.0001). (c) Day 8 intrathecal MRS5698 injection in the absence of morphine. Mor + Veh n = 5, Mor + MRS5698 3 nmol n = 6, Mor + MRS5698 25 nmol n = 5, Mor + MRS5698 50 nmol n = 6. Two-way ANOVA, Dunnett’s post hoc test (Interaction F(6,36) = 1.404, p = 0.2398; Time F(2,36) = 503.9, p < 0.0001; Treatment F(3,18) = 0.2733, p = 0.8438). No significance at each timepoint. (d) Morphine dose-response curves and (e) median effective dose (ED50) calculated on day 13. Intrathecal MRS5698 (50 nmol) or vehicle was administered with the first morphine injection. D1–12 ip Saline n = 5 for all groups, D1–12 ip Morphine n = 6 for all groups. One-way ANOVA, Sidak’s post hoc test F(7,36) = 63.13, p < 0.0001. *Comparisons as indicated (Mor + Vehicle + D13 MRS5698 i.t. vs. Mor + Vehicle + D13 Vehicle i.t. p = 0.0003, Mor + MRS5698 + D13 MRS5698 i.t. vs. Mor + MRS5698 + D13 Vehicle i.t. p < 0.0001). NS, not significant. All data are presented as mean ± SEM
